Kia ora (a traditional Māori greeting), my name is Natasha Barrett and I’m Museum Studies PhD student from the University of Leicester (AHRC Midlands 3 Cities funded). My research is about colonial-era photographs (1860s-1914) of Māori, the indigenous Polynesian people of New Zealand. I have been discovering how these photographs have been understood and used over time by both Māori and non-Māori. This includes within and outside of British museums. I approach photographs as three-dimensional physical objects. They can as my research shows, reflect social connections amongst communities and with institutions around the world holding photographic collections.
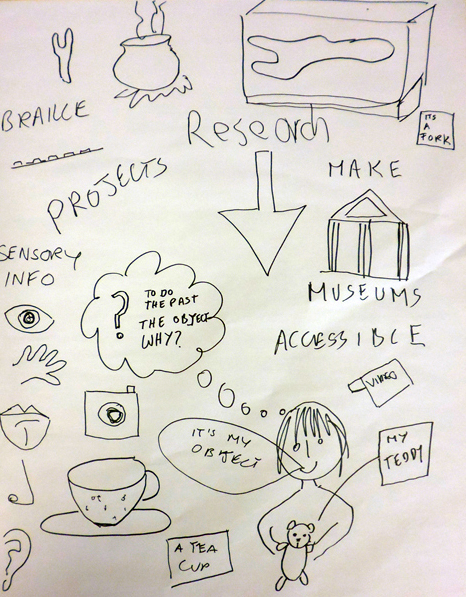
A few months ago, as part of my PhD fieldwork, I met up with Dr Kate Allen at the British Museum. Despite our projects seeming quite dissimilar, there were many parallels, which were helpful for my research. For example, groups of people (and individuals) understand the world in very different ways and all are equally valid. The challenge for those of us working in museums is to try and understand this. We then need to create space for alternative ways of explaining objects. Sensory Labels fully and cleverly achieves this.
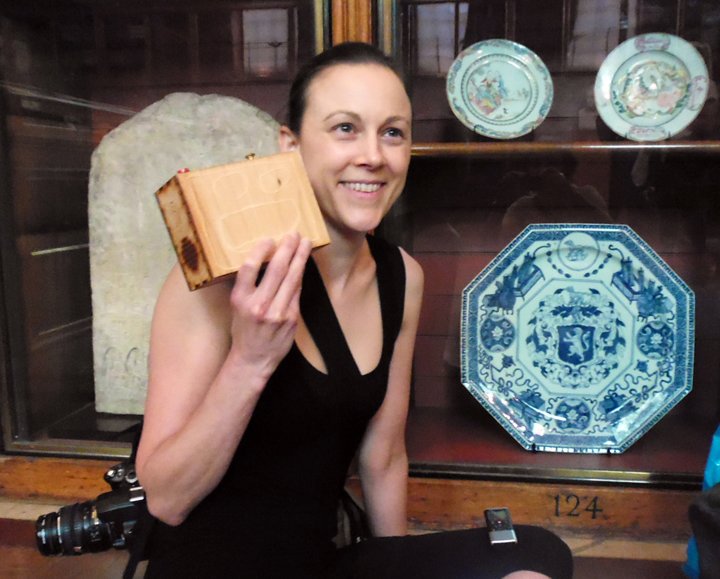
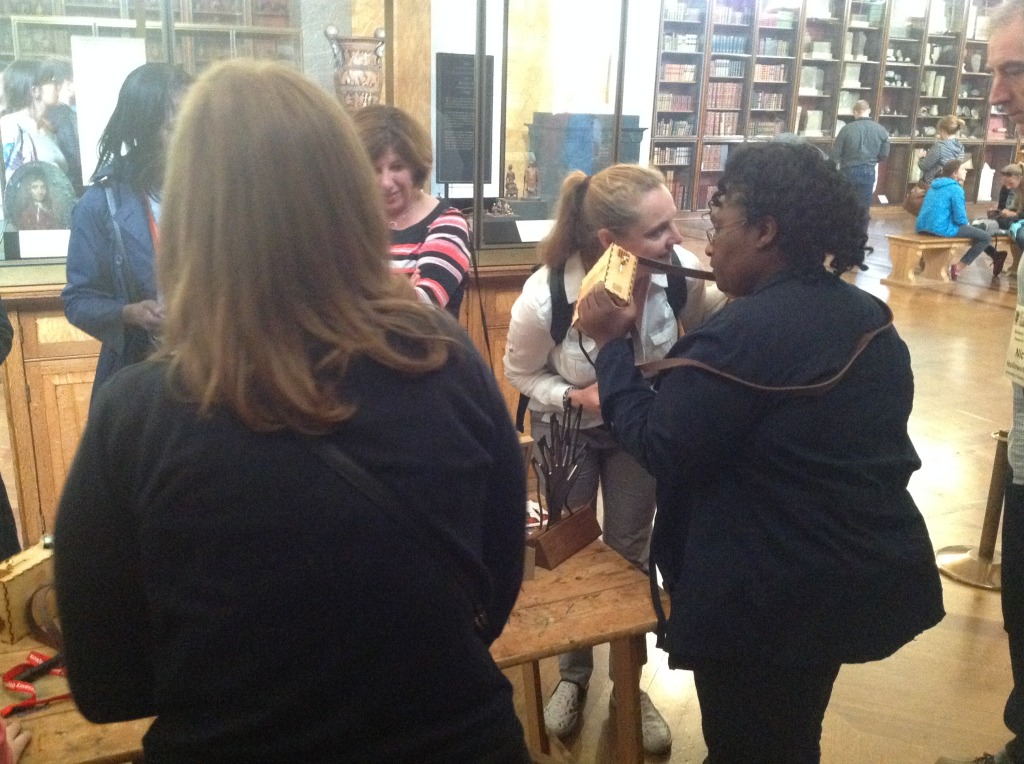
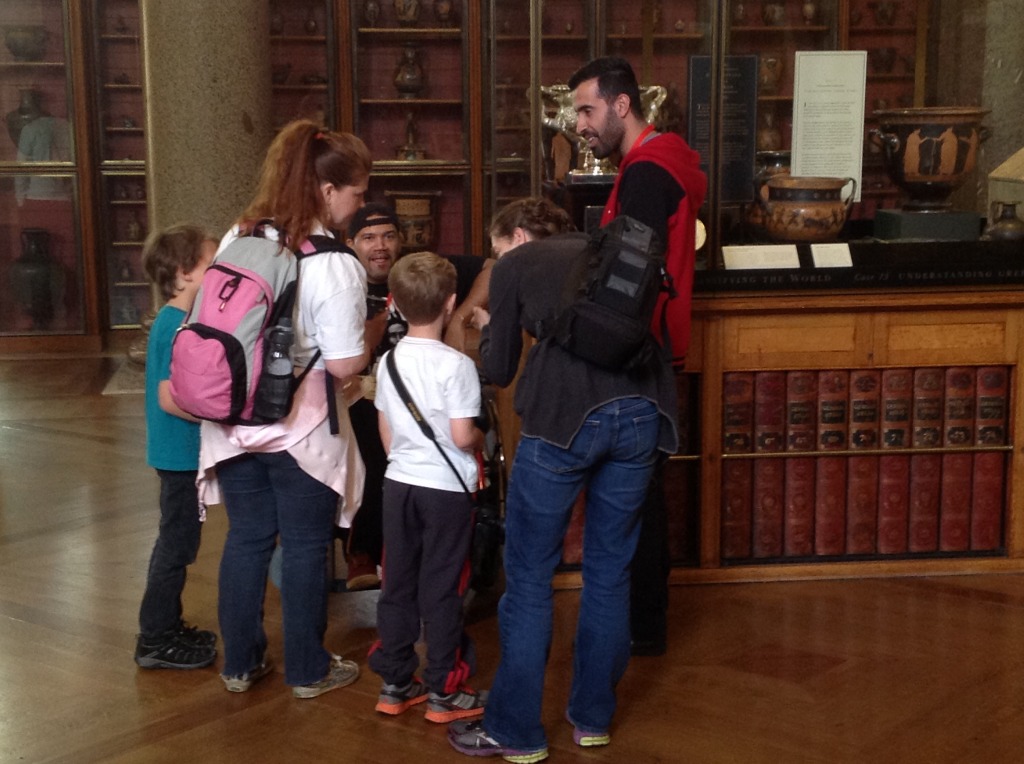
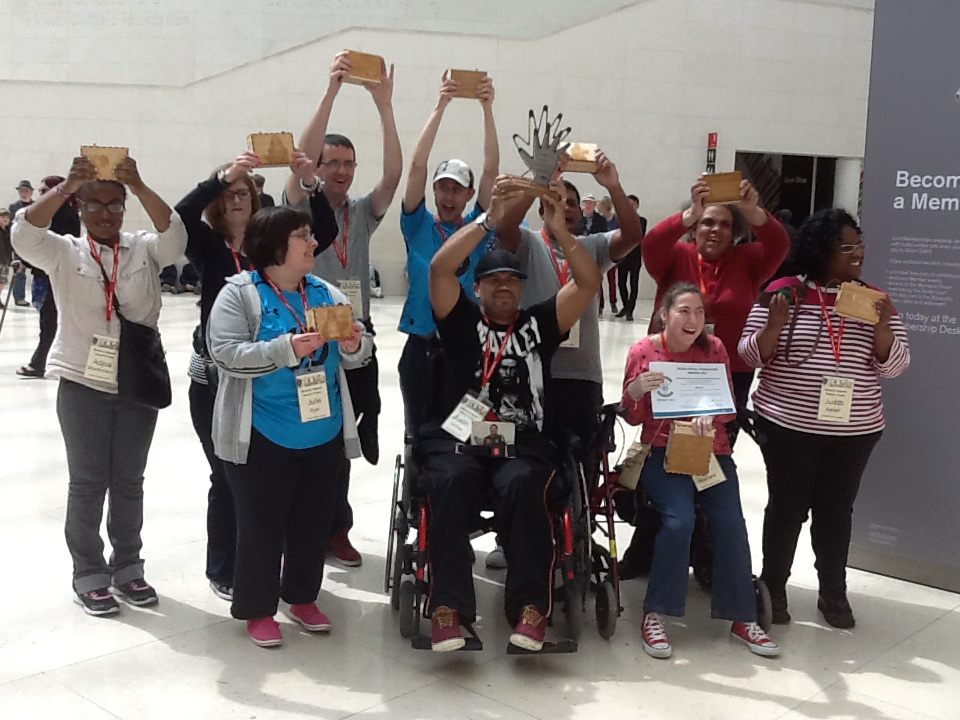
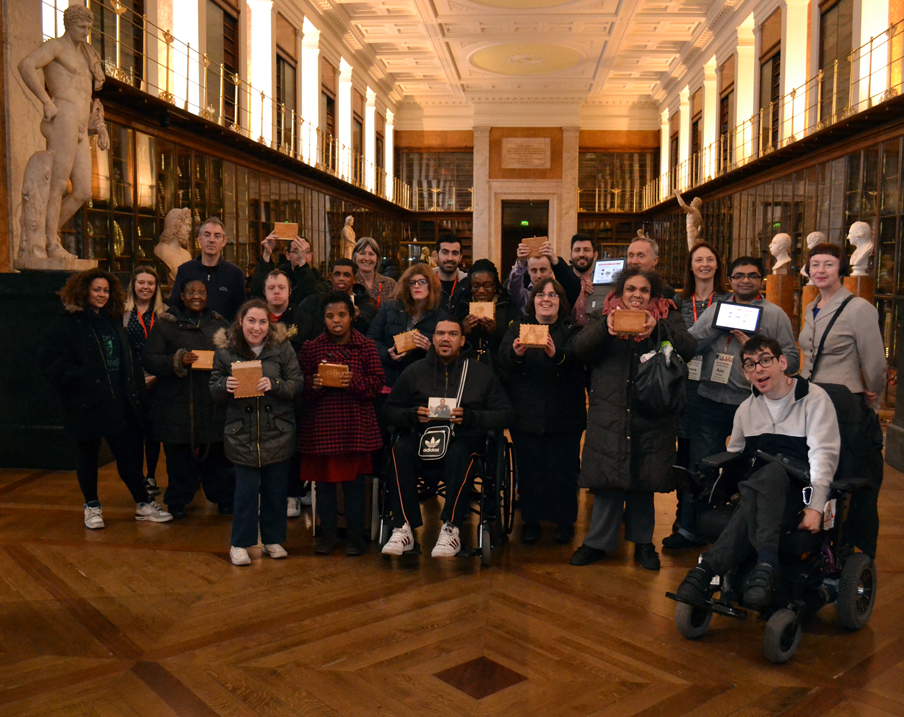
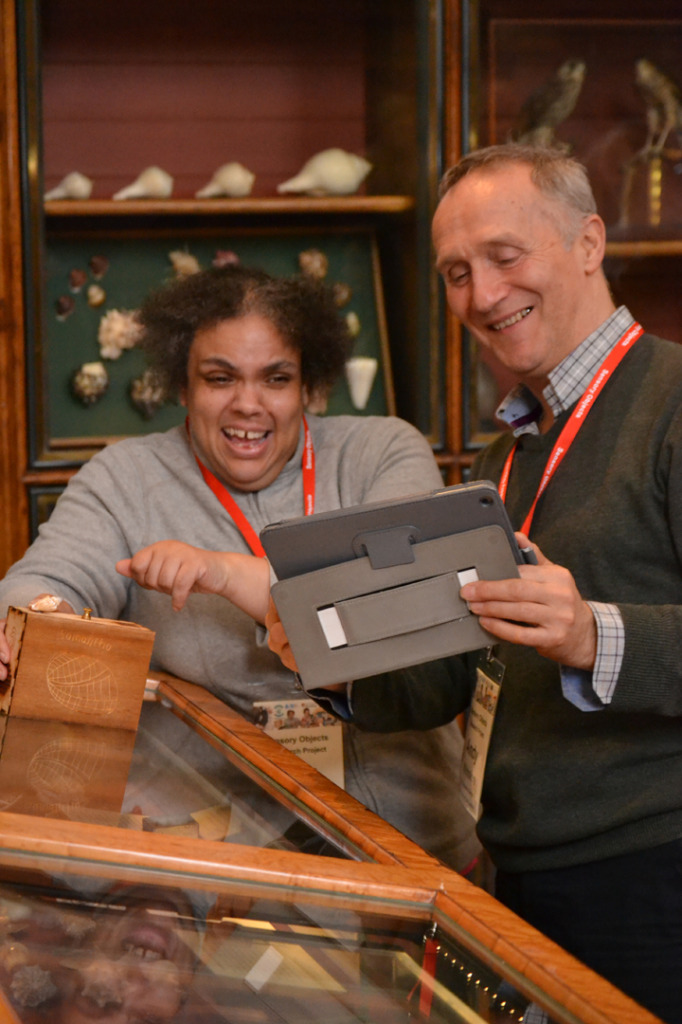
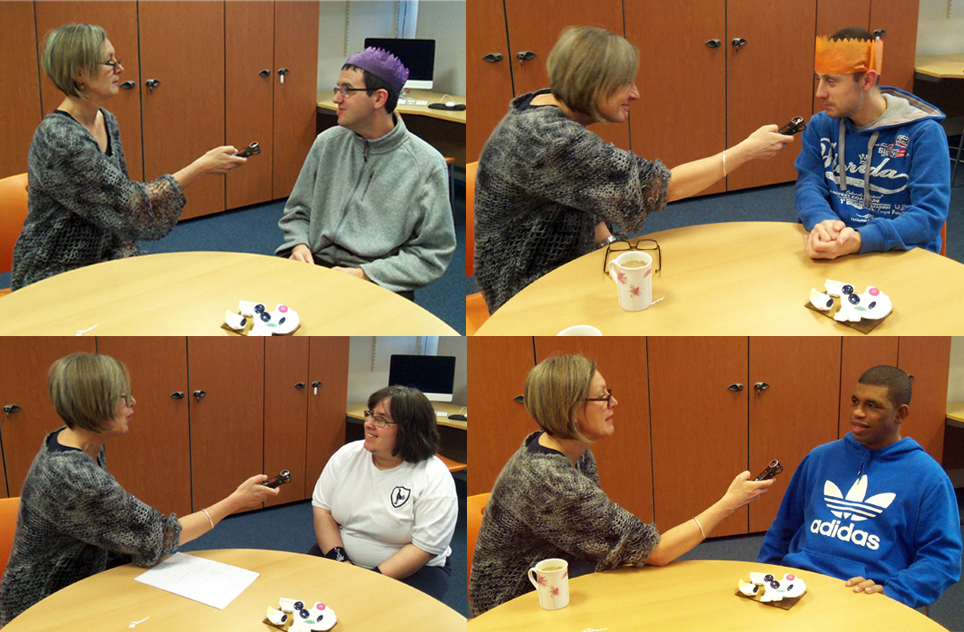
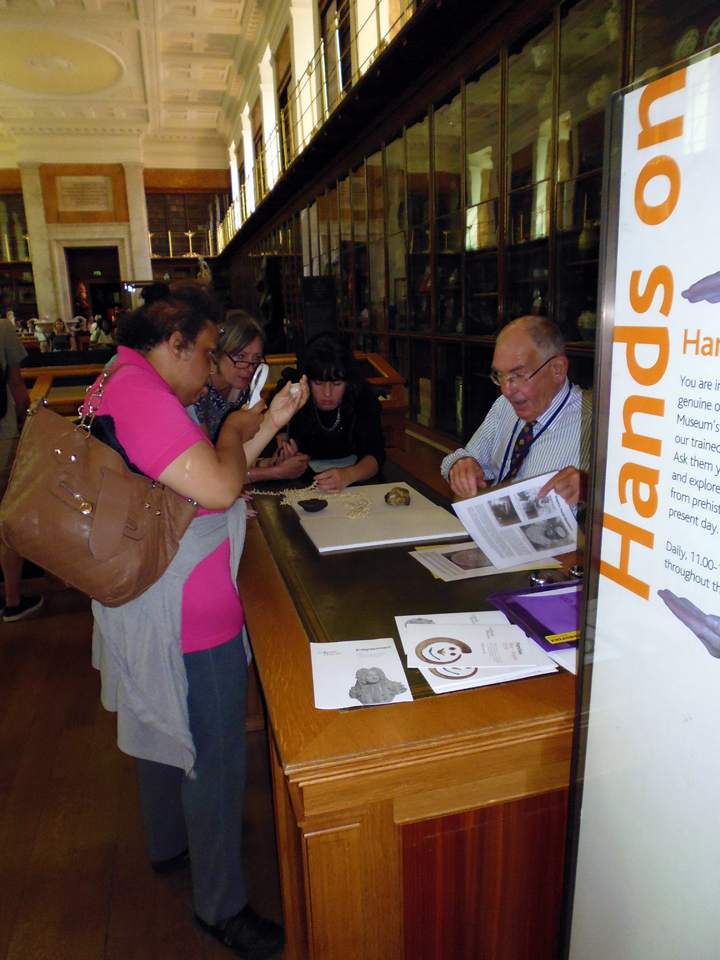
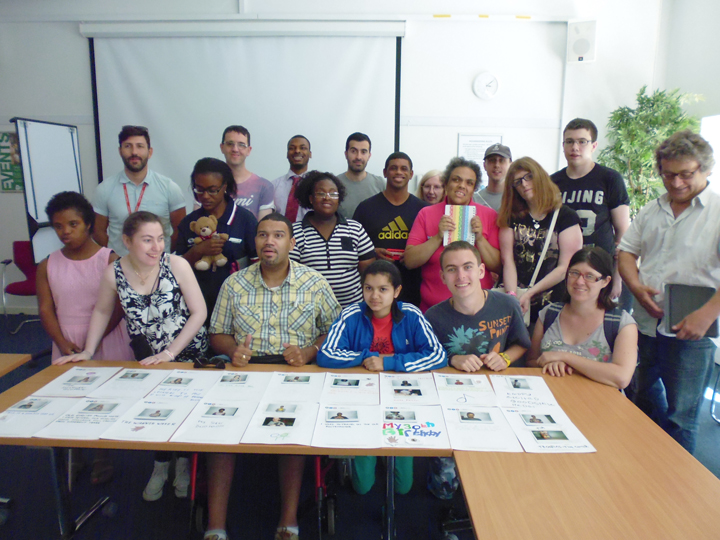
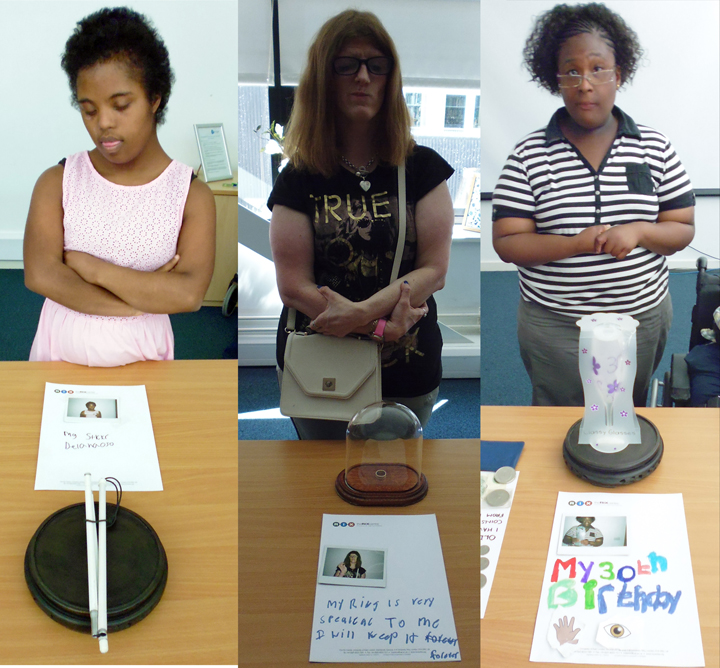
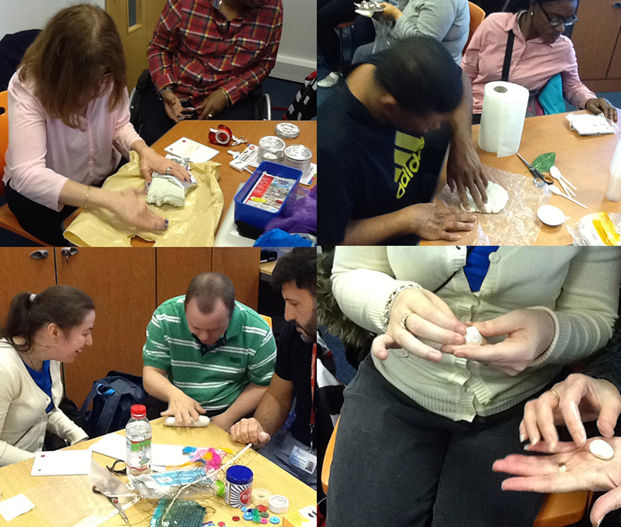
Kate gave me a tour around the Enlightenment Gallery with a few of the Sensory Labels. Having recently found out I am dyslexic, I was also personally interested to experience interpretation that does not use text. I was immediately struck by the wonder of the experience and sat with the labels on the gallery floor listening, smelling, touching, smiling and laughing. Through the labels I entered into the stories of the creators – the personal associations, meanings and memories that the objects in the gallery held for them. Each Sensory Label is highly unique, beautifully crafted and reflects the creator’s personality. By the end, I felt I had ‘virtually’ met a fascinating group of people who had enriched my experience of the gallery.
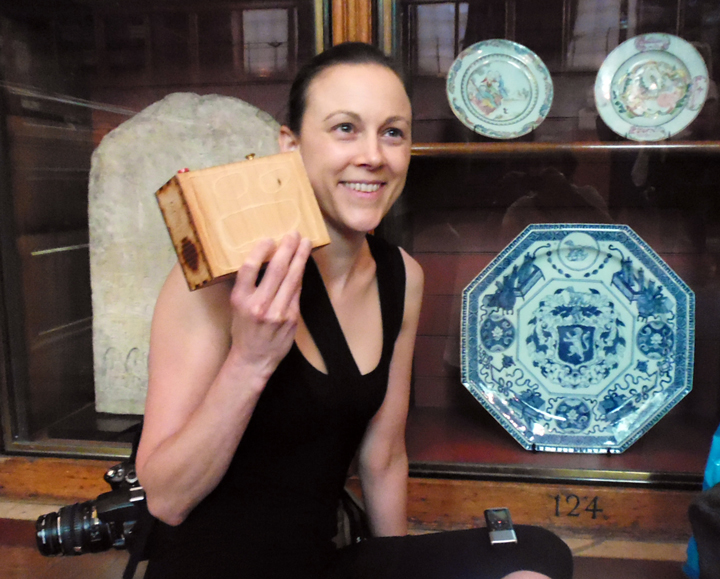
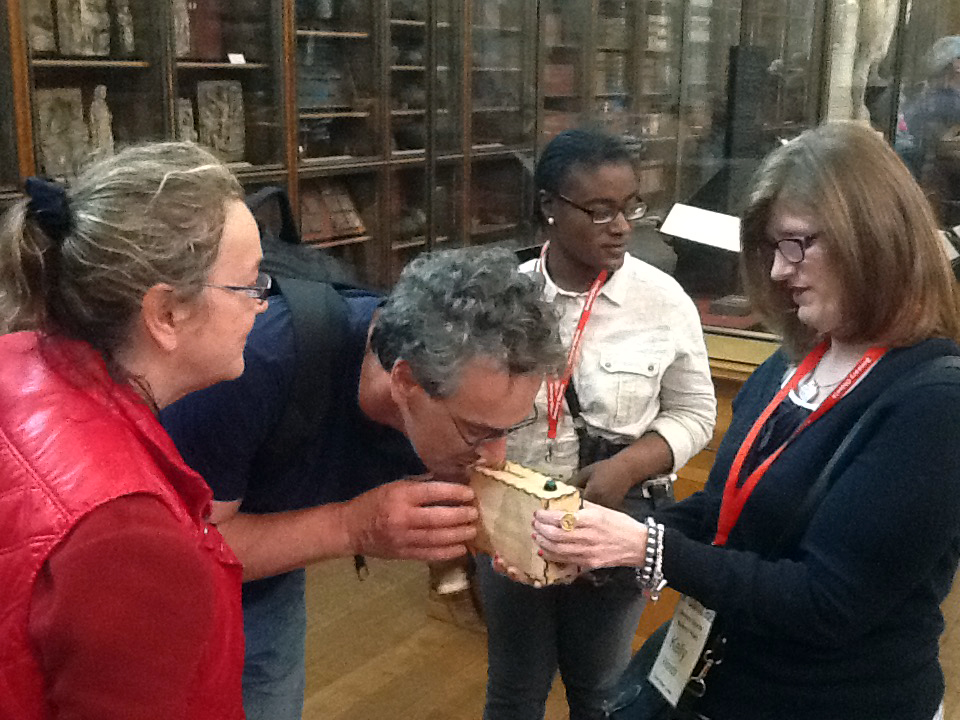
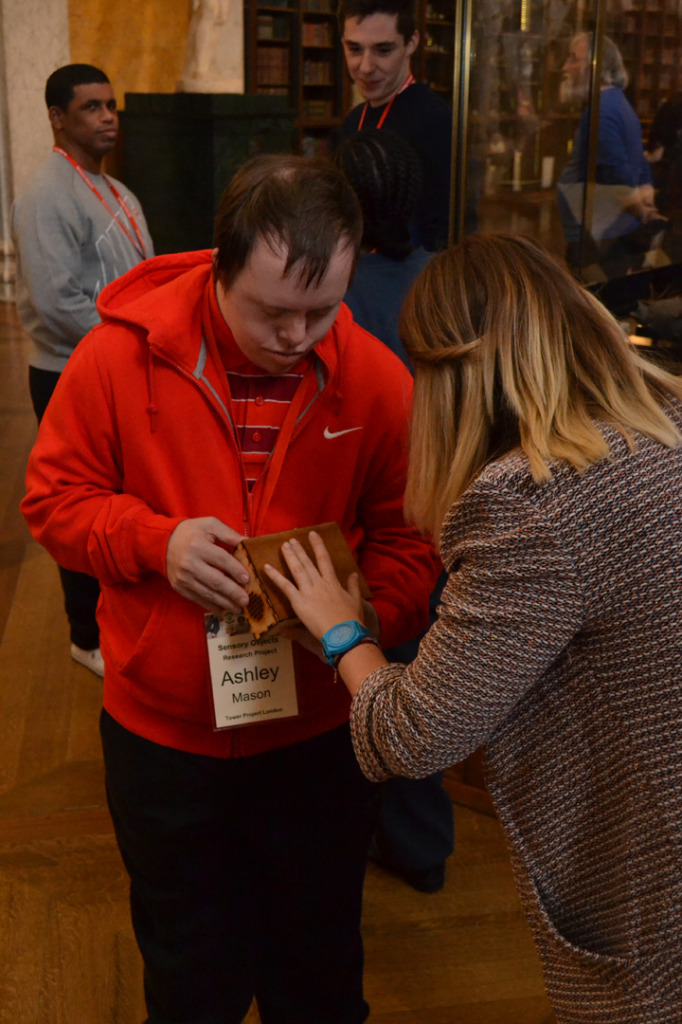
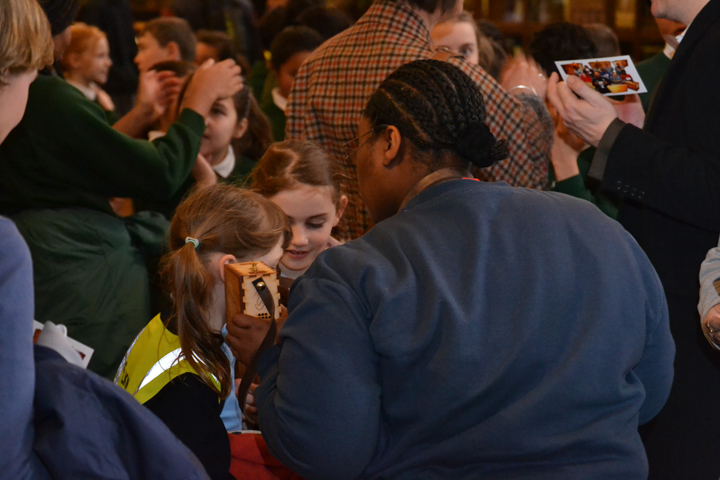
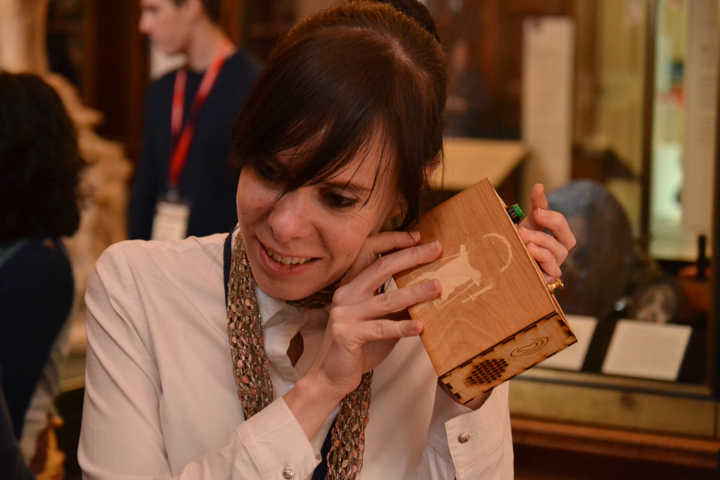
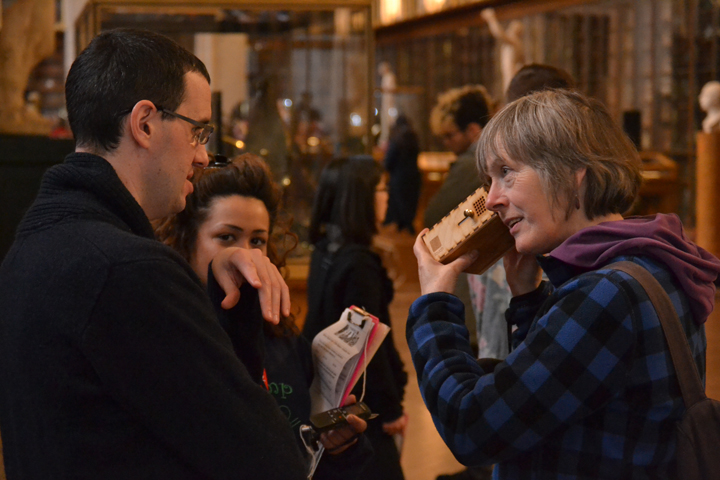
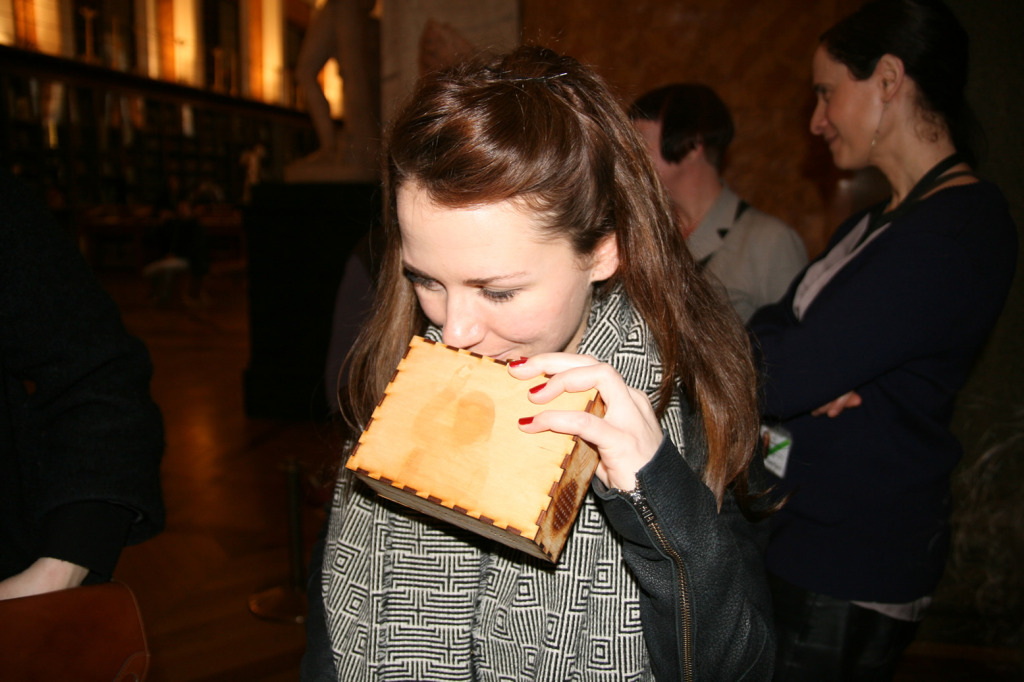
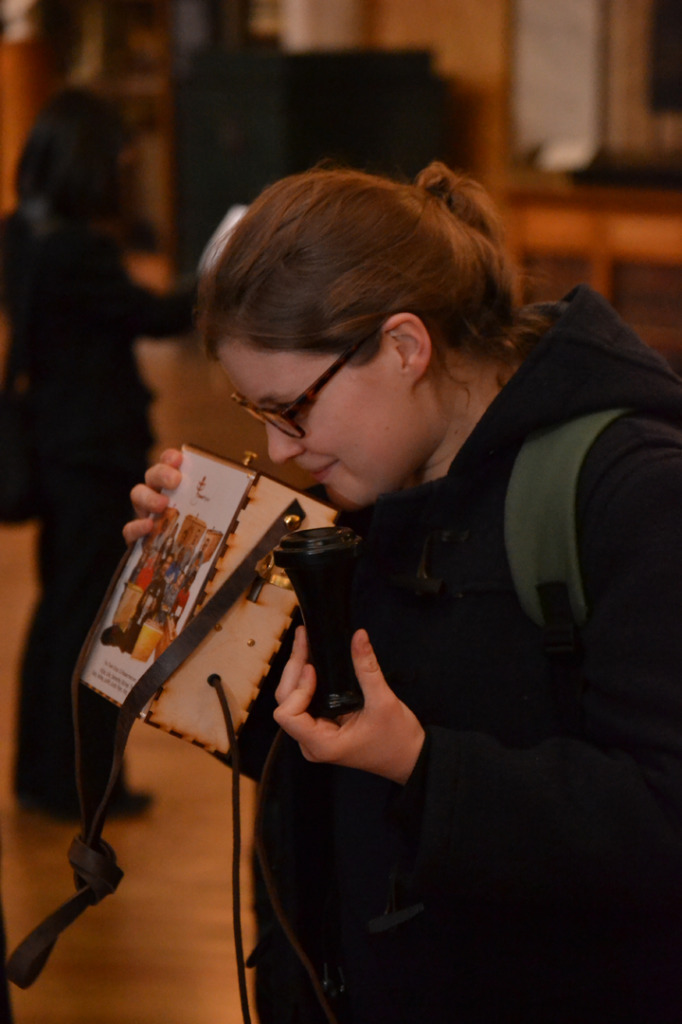
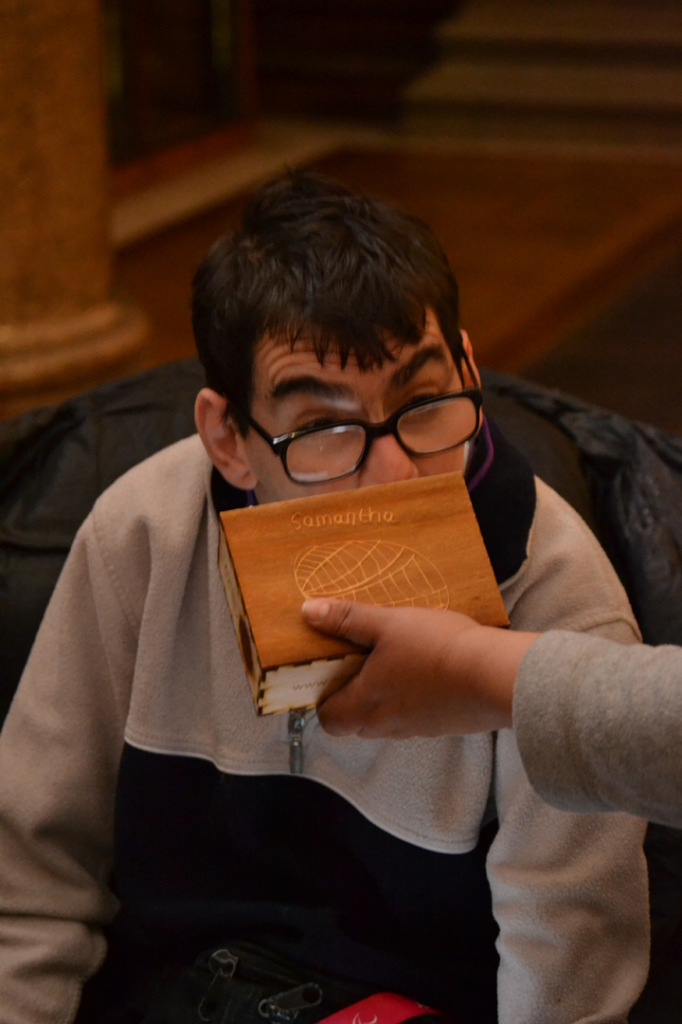
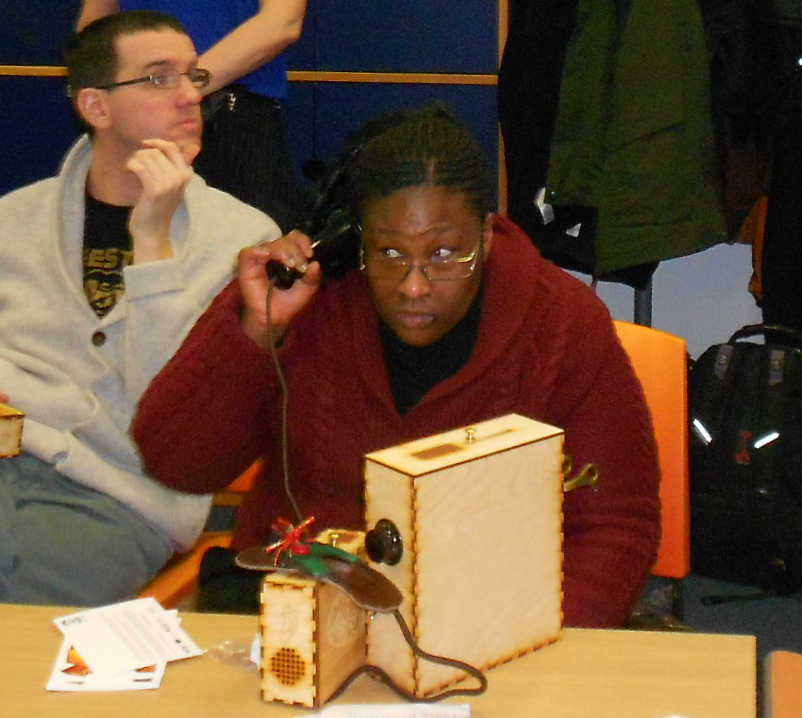
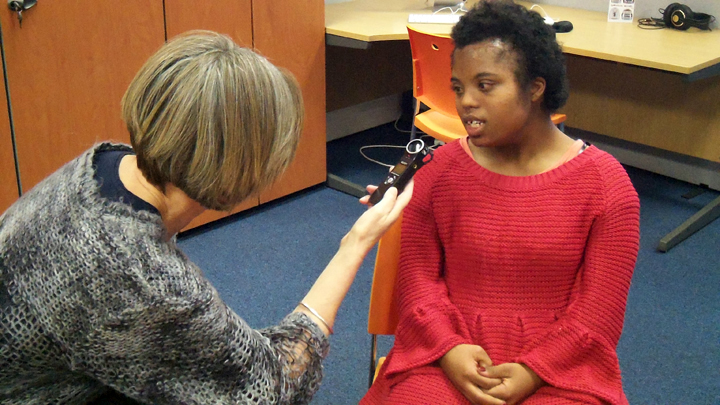
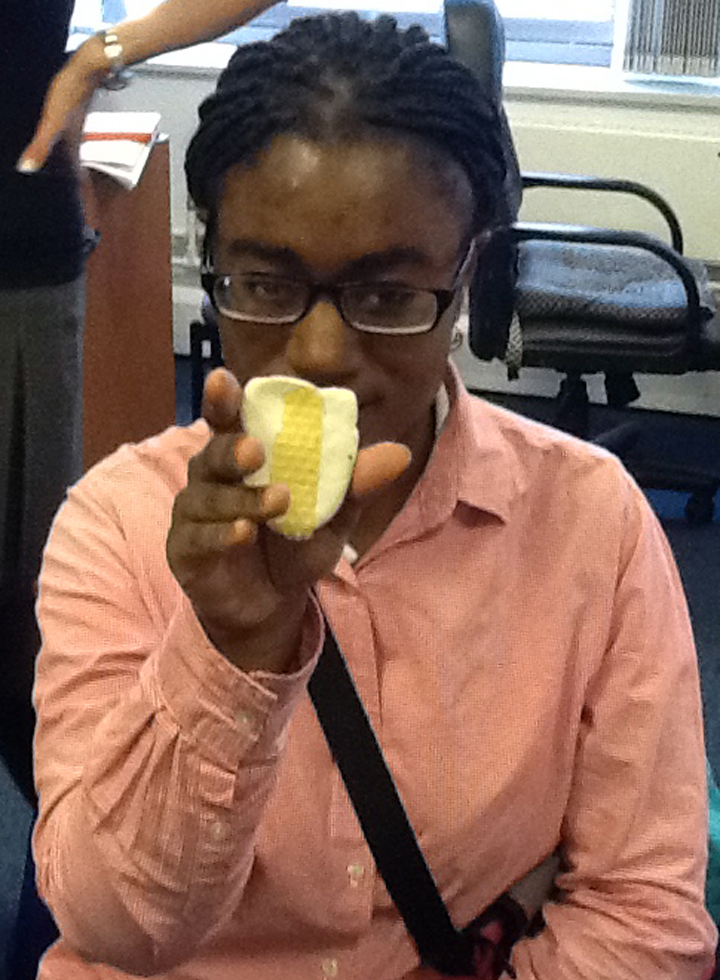
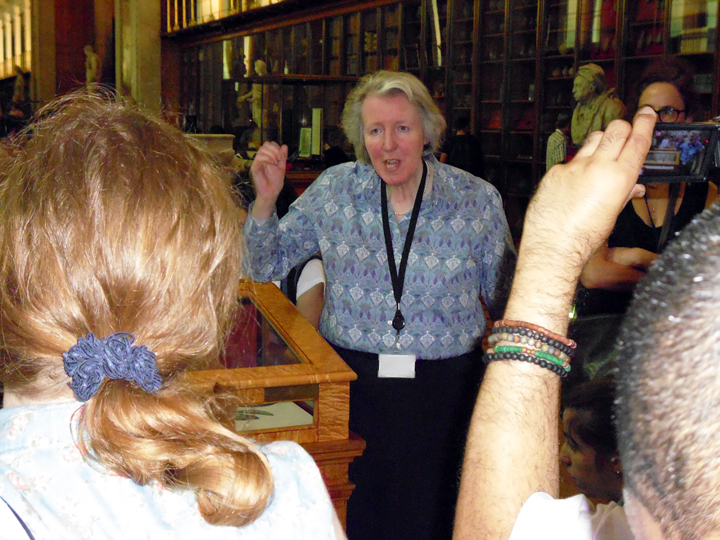
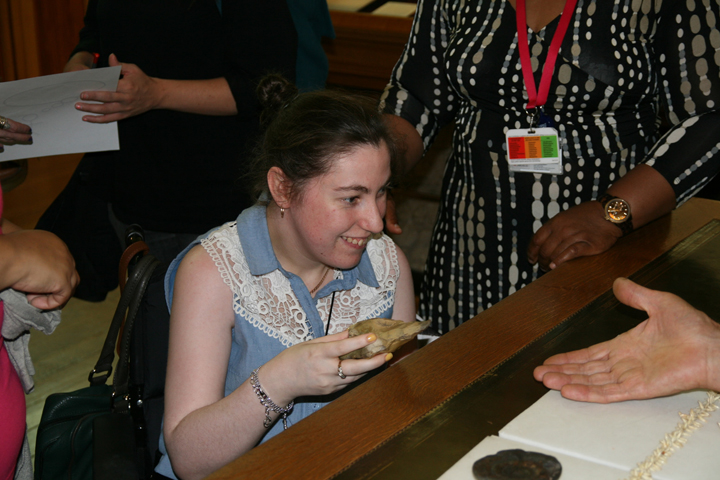
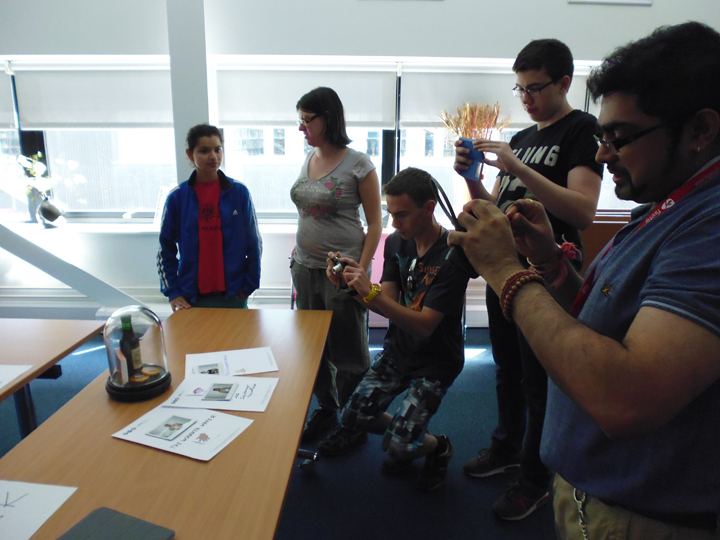
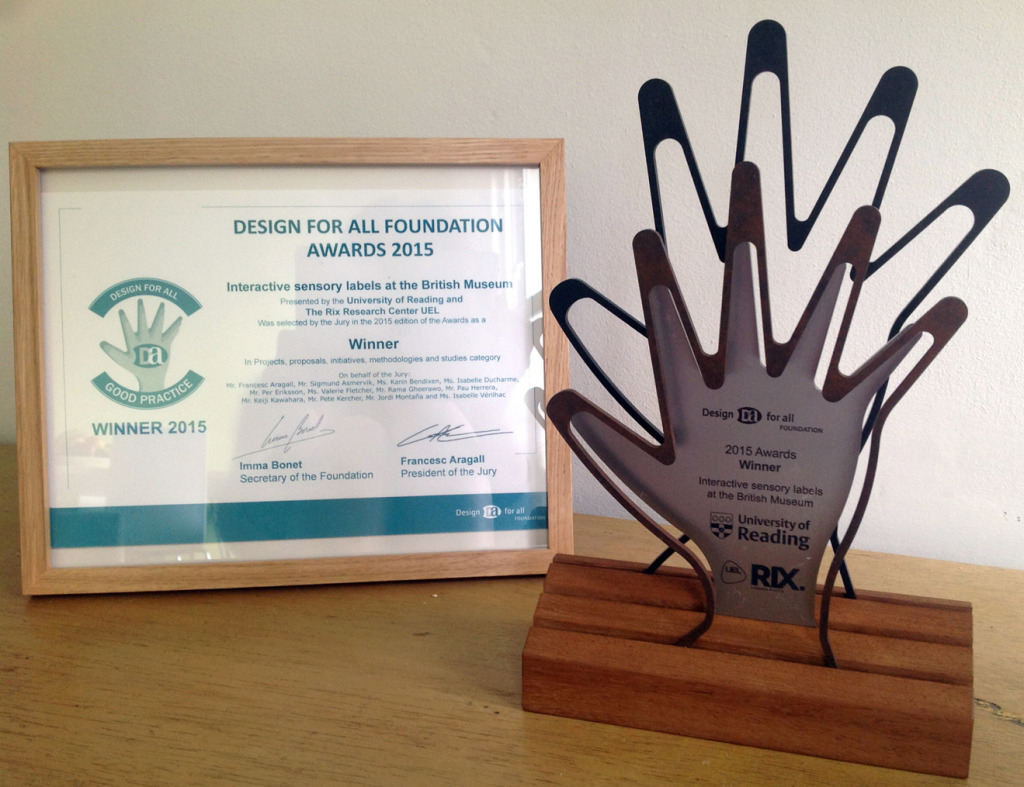
The author listening to Ryan Burns’ Sensory Label, 2016. Photograph courtesy of Dr Kate Allen.
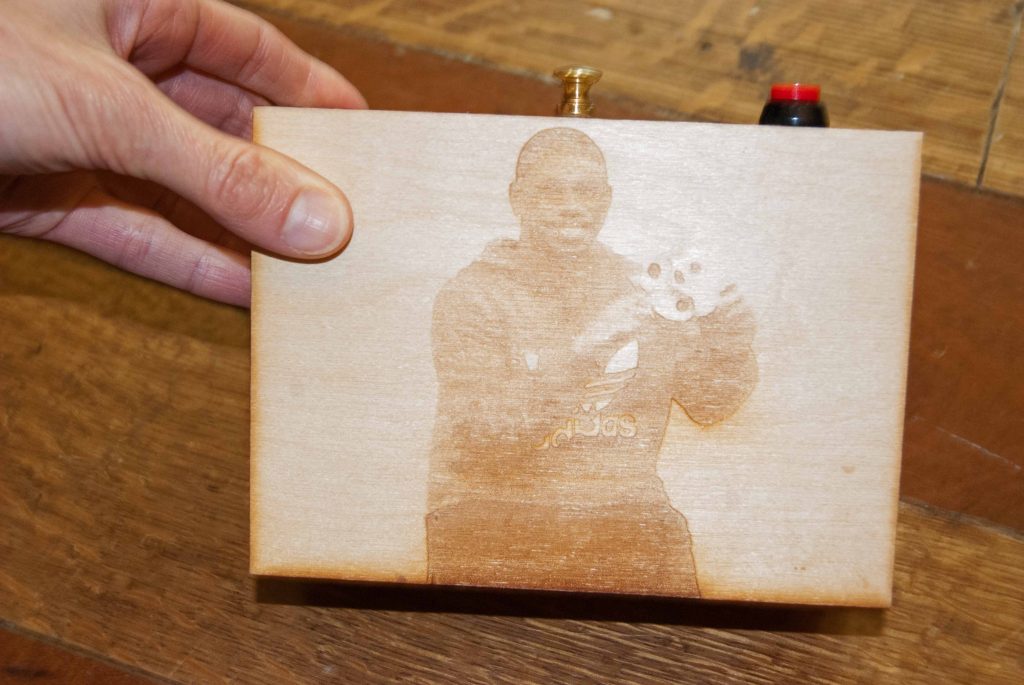
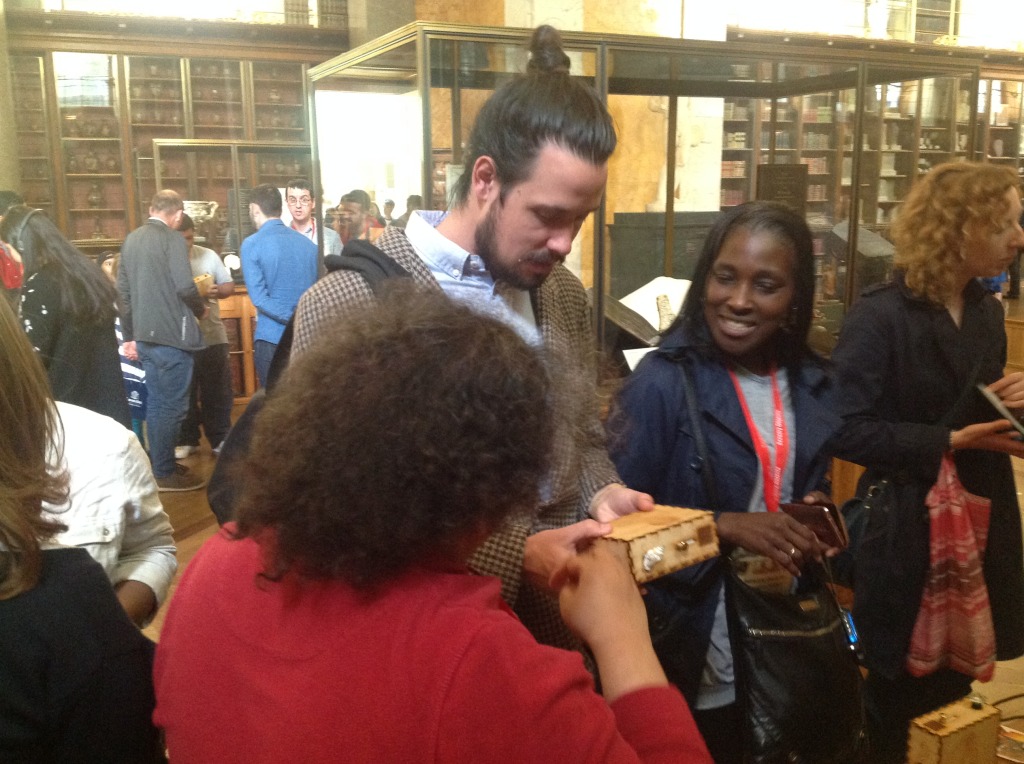
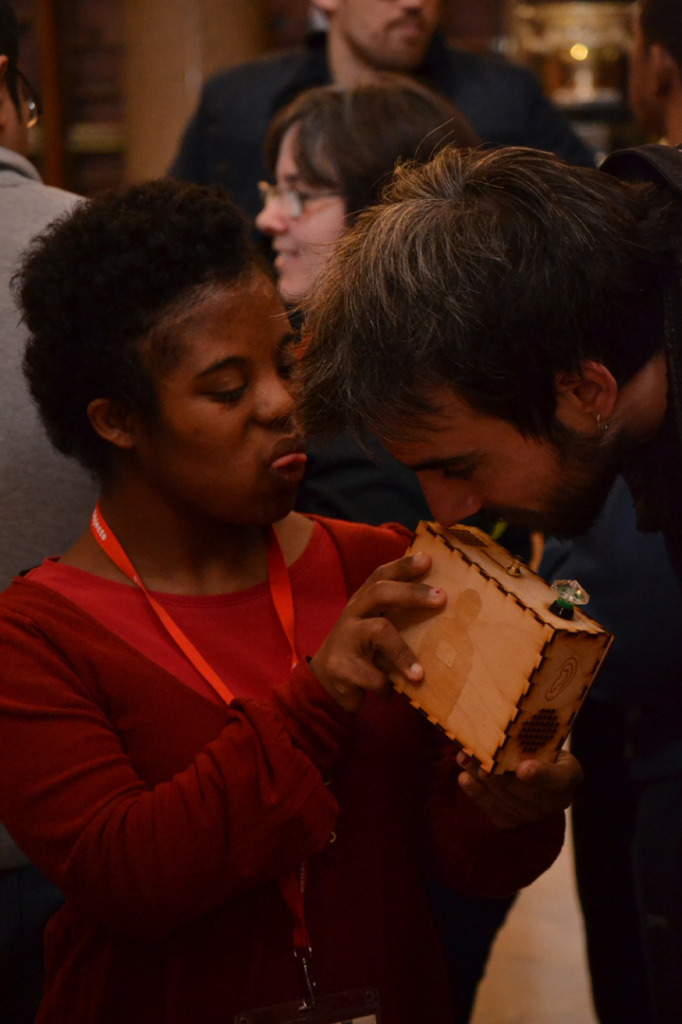
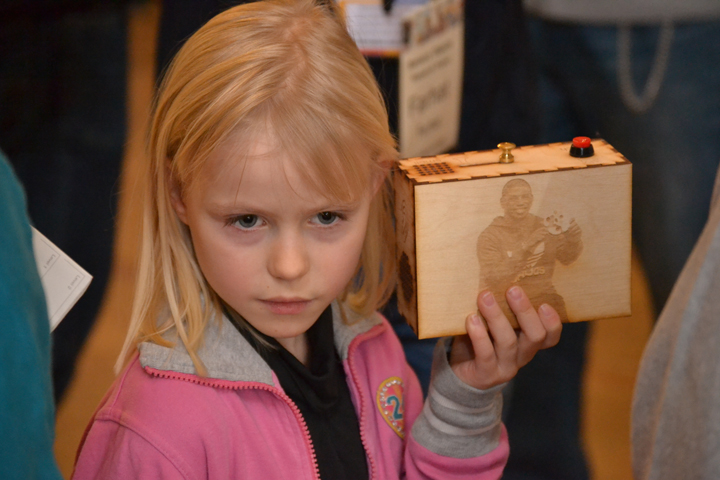
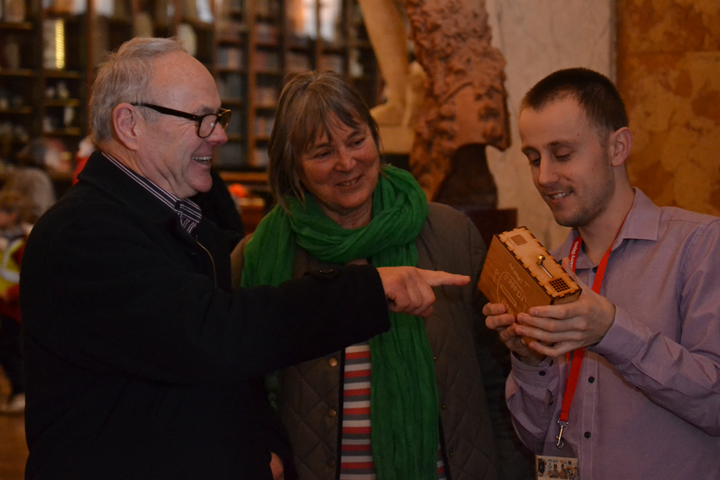
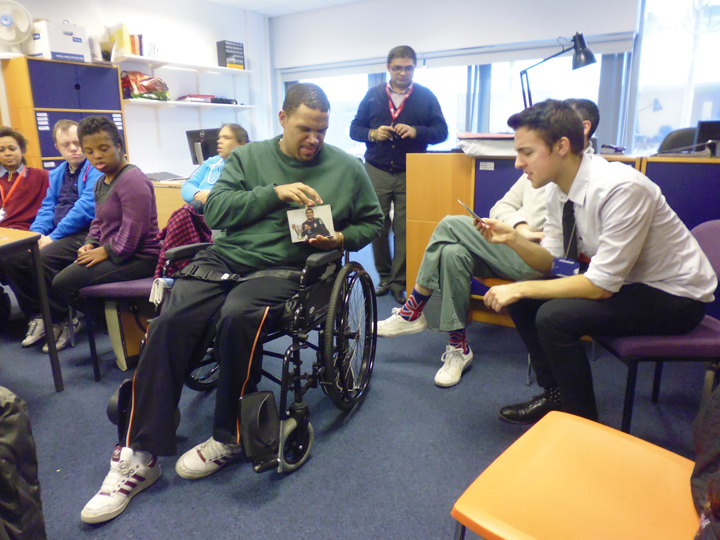
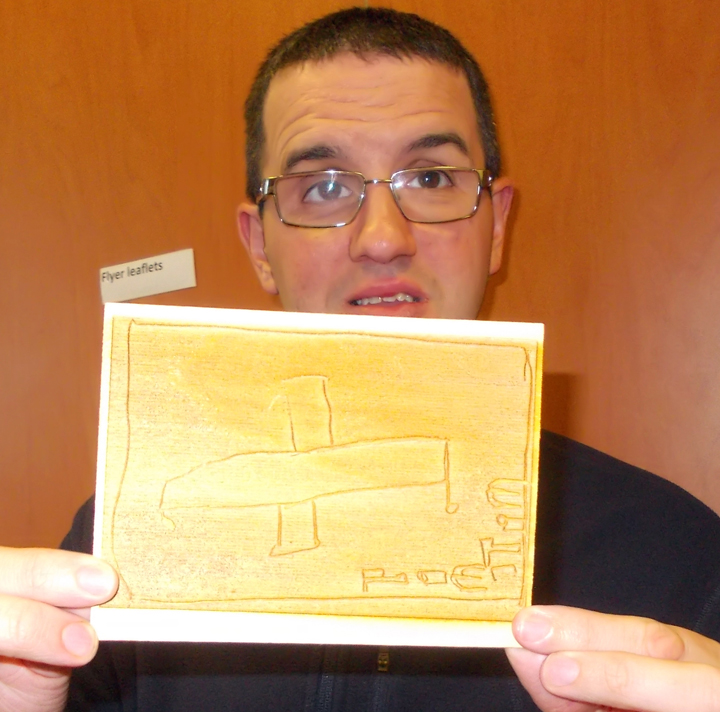
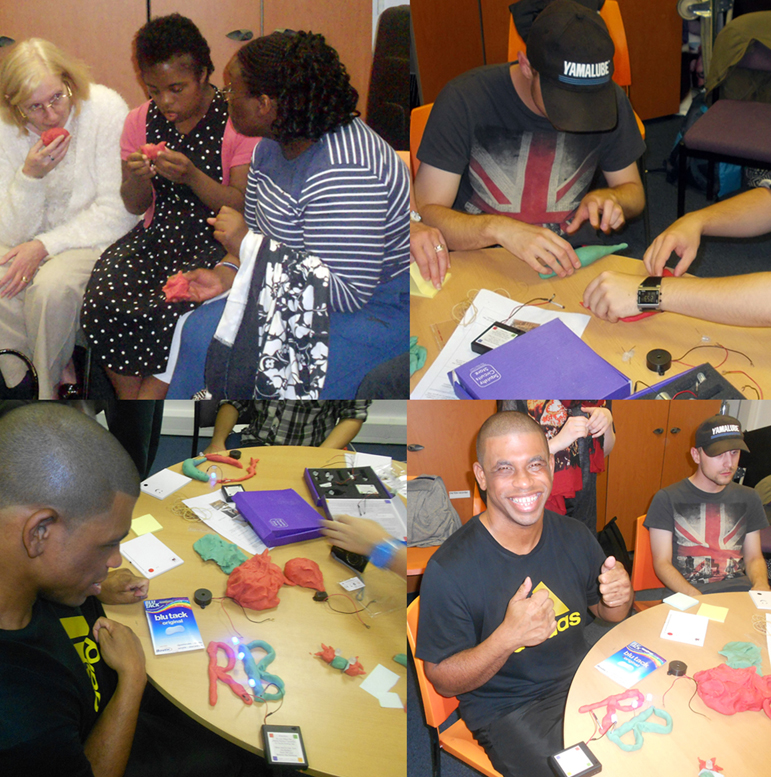
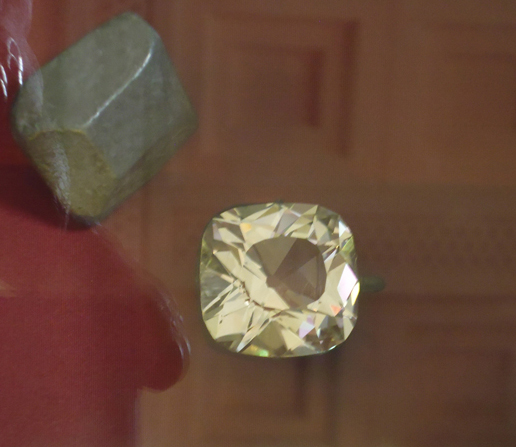
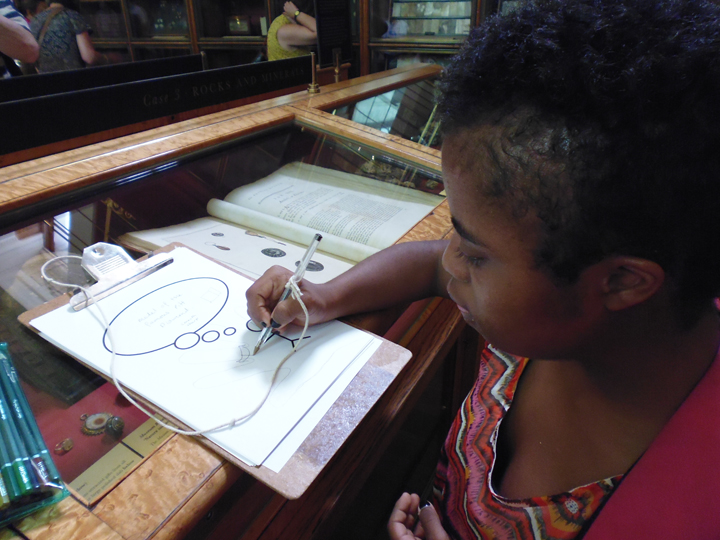
Ryan Burns’ Sensory Label showing his laser cut photograph, 2016. Photograph by Natasha Barrett.
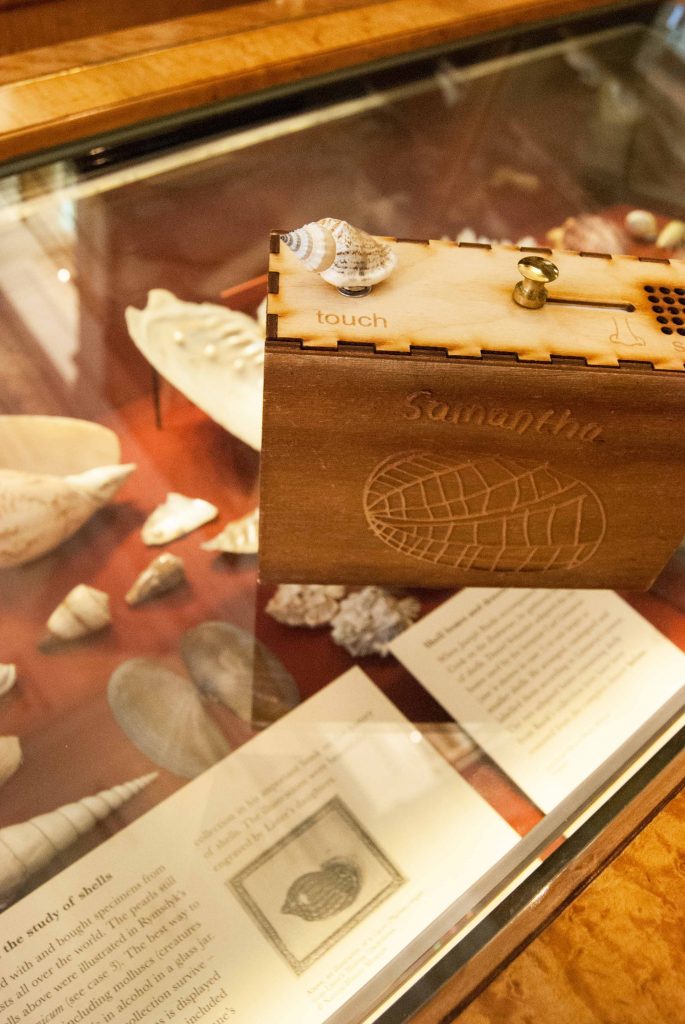
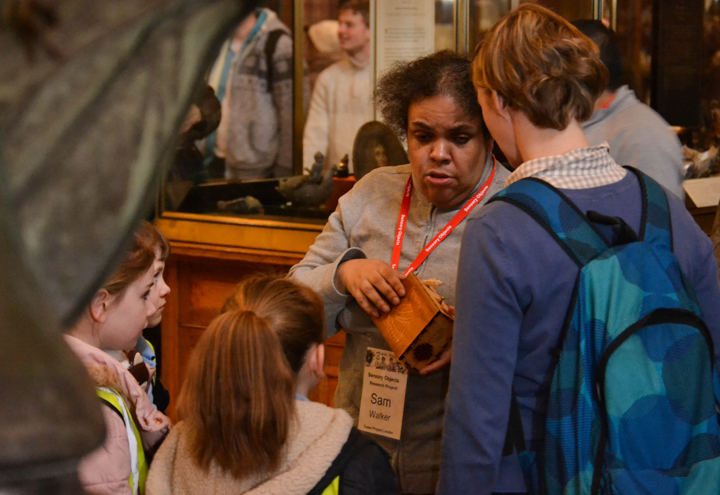
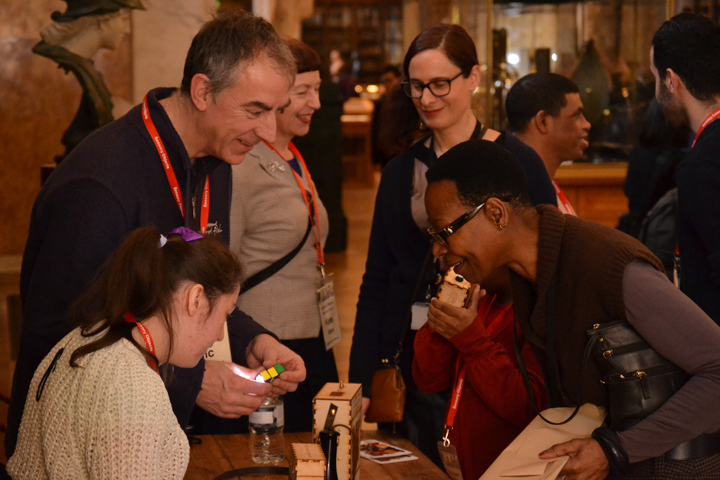
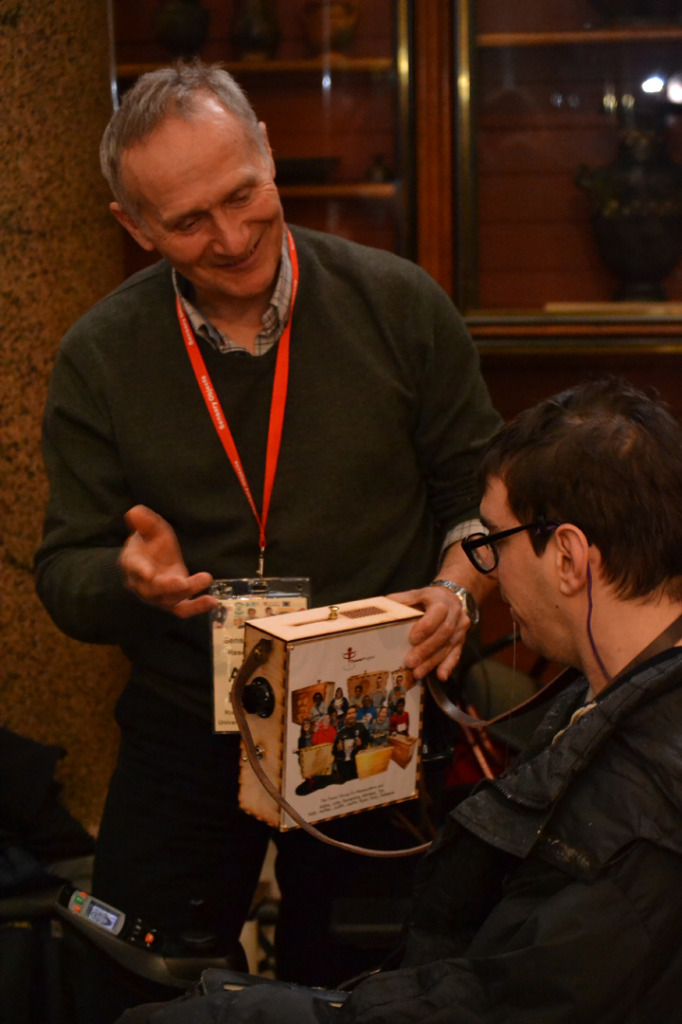
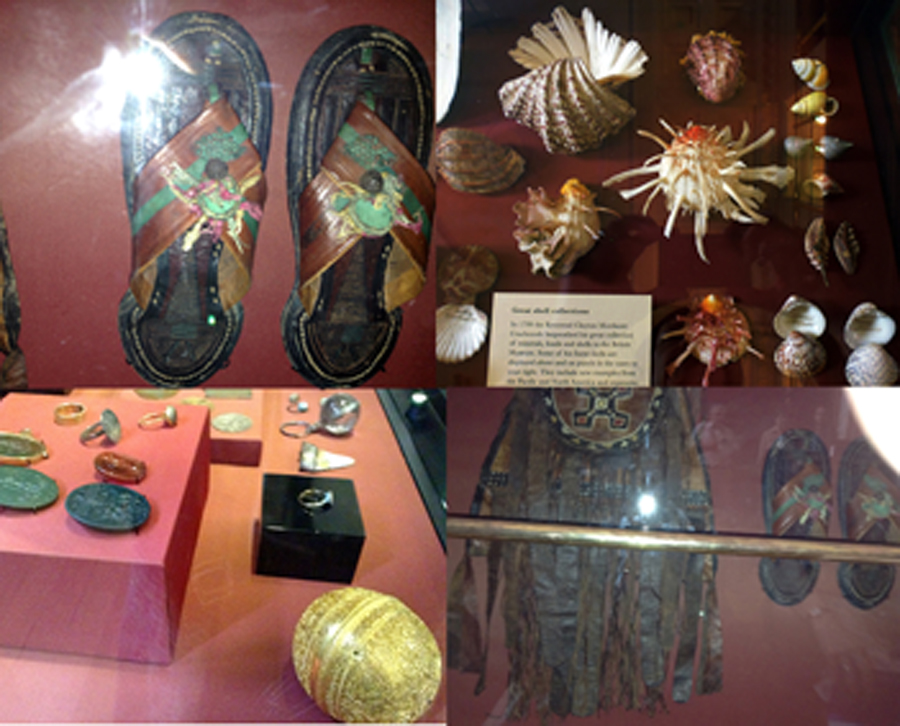
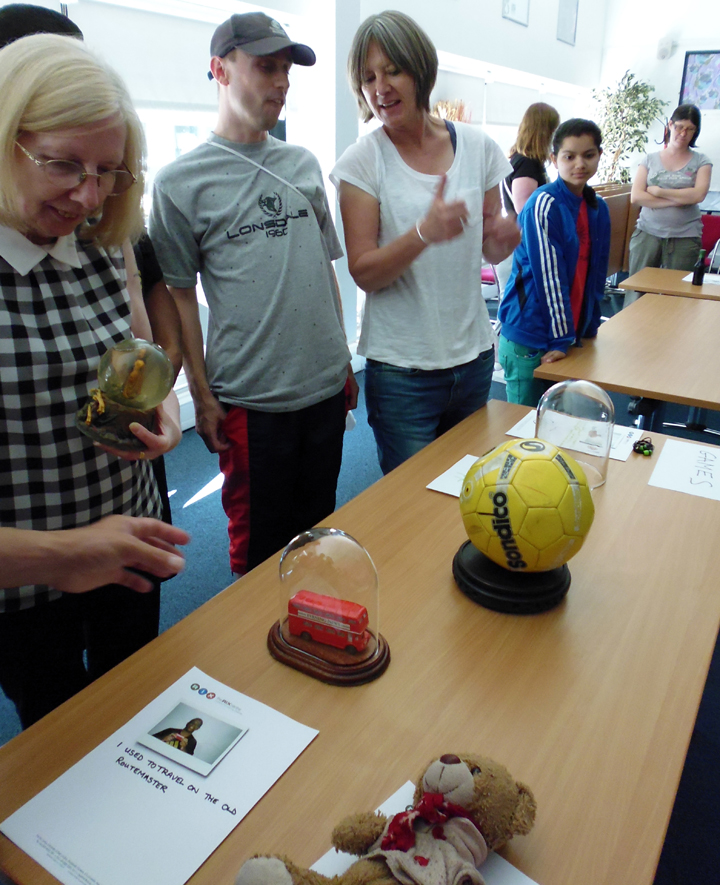
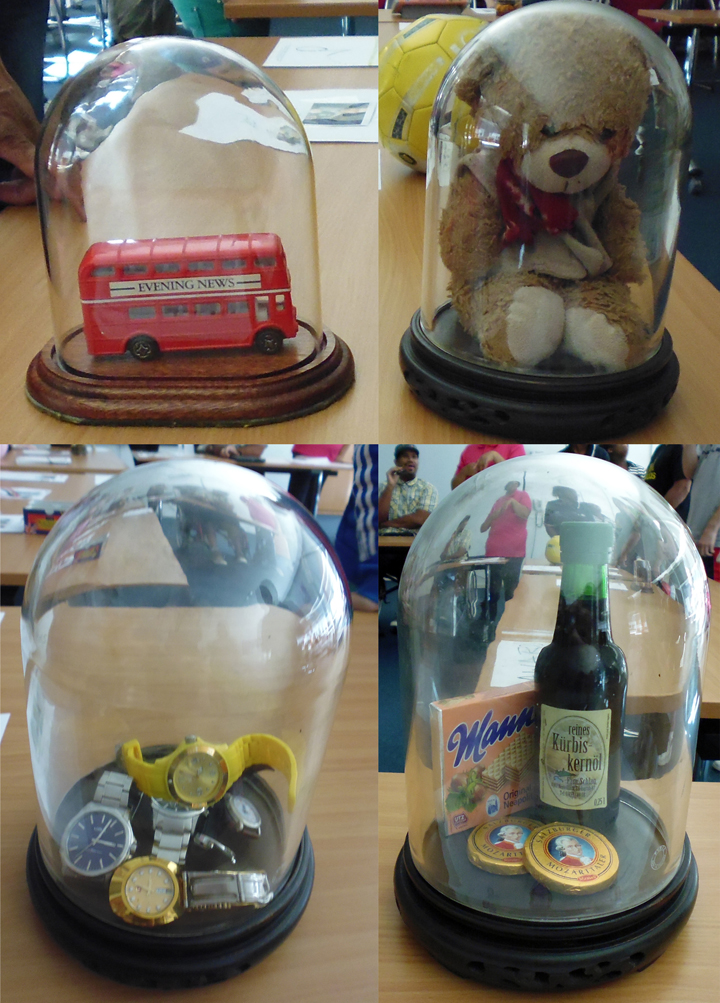
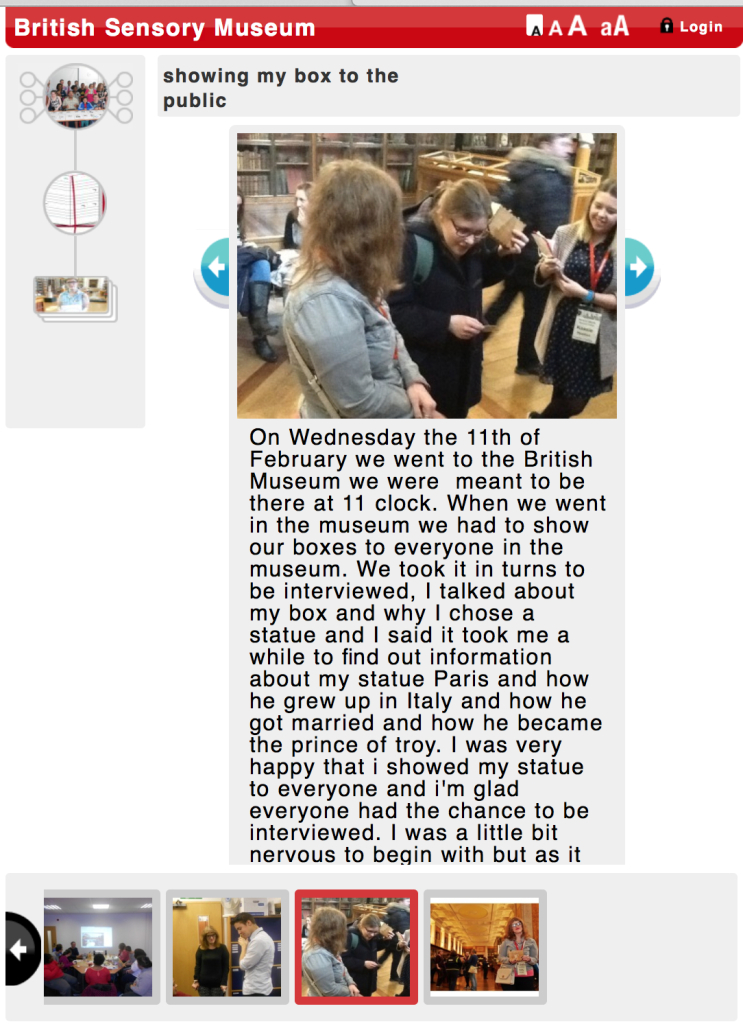
The labels, many of which include miniature versions of the displayed objects, emphasise the sense of touch. Usually in galleries you can only imagine what touching the objects behind glass might be like. Sam Walker’s use of a real shell and Judith Appiah’s carefully crafted Nigerian slipper let you experience the feel of the objects – their texture, shape and smell. Far from being just interpretative devices, Sensory Labels are also fascinating objects in their own right. Not only did they hold my attention but they drew in other people in the gallery, including one of the museum guides. We had a fascinating discussion about snakes in the Hindu religion, as a result of Katy Woollard’s snake themed label. This is, as Kate and I discussed, the power of the Sensory Labels. They create opportunities for conversations and let people share knowledge and diverse perspectives.
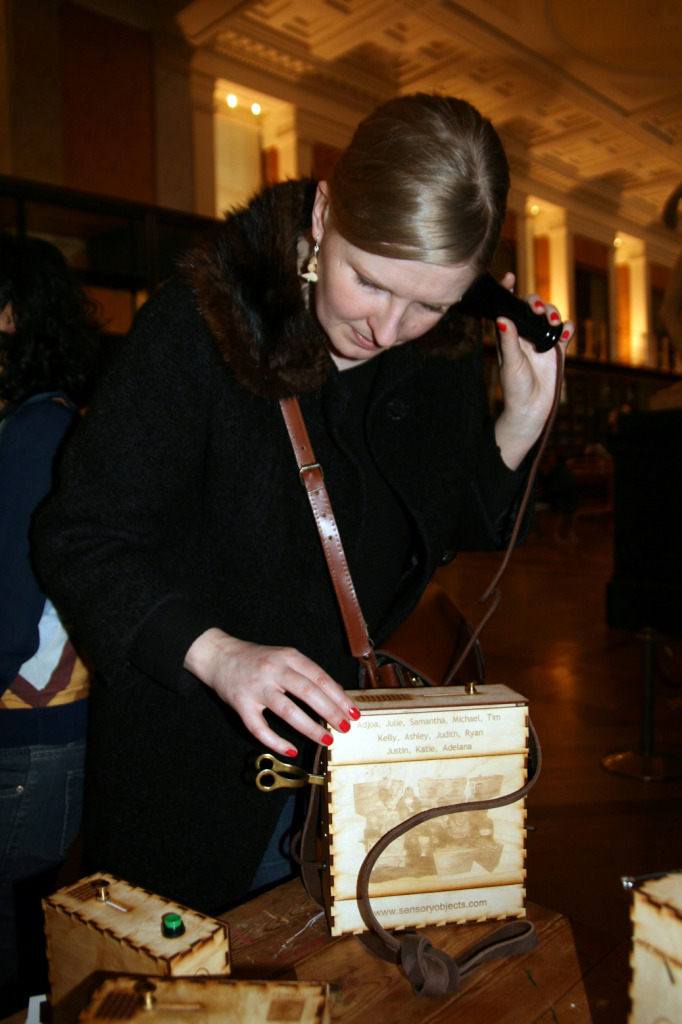
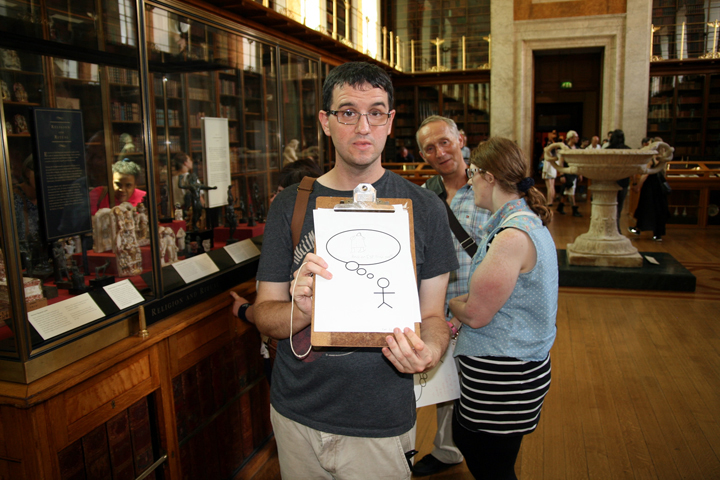
Sam Walker’s Sensory Label with shell on/off switch, 2016. Photograph by Natasha Barrett.
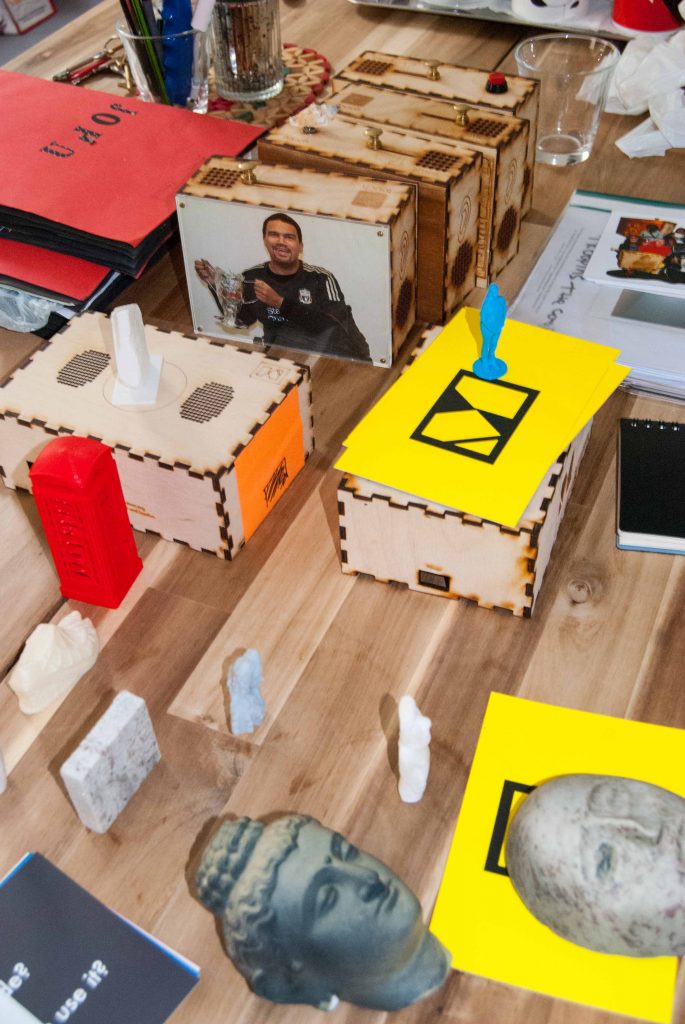
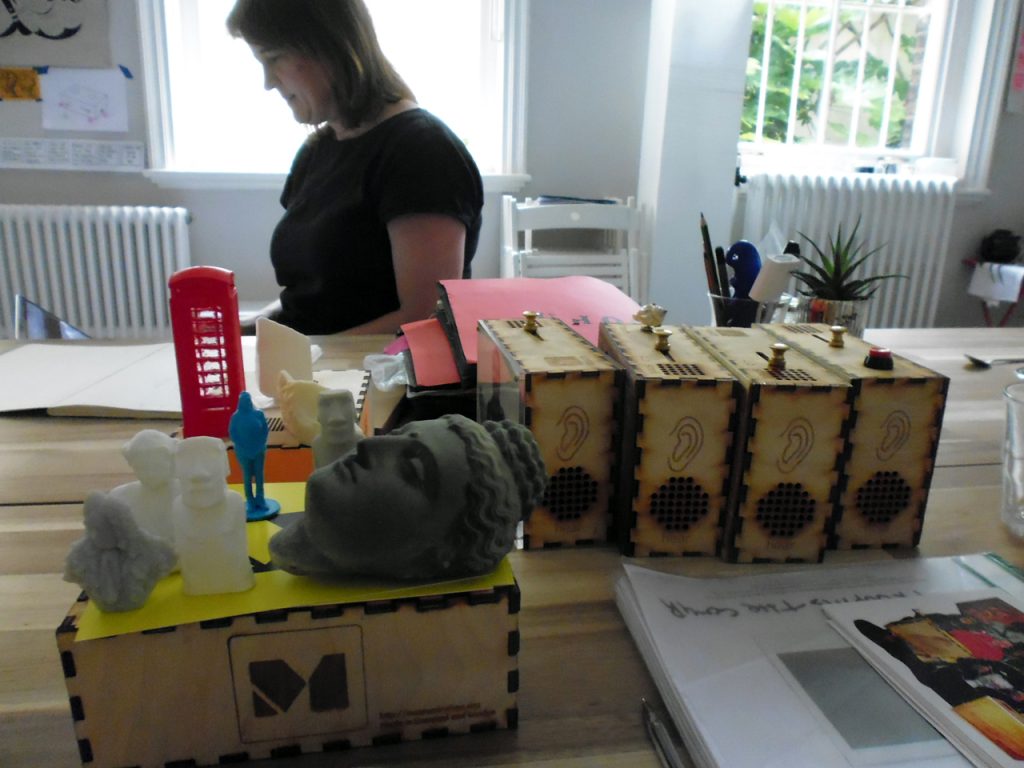
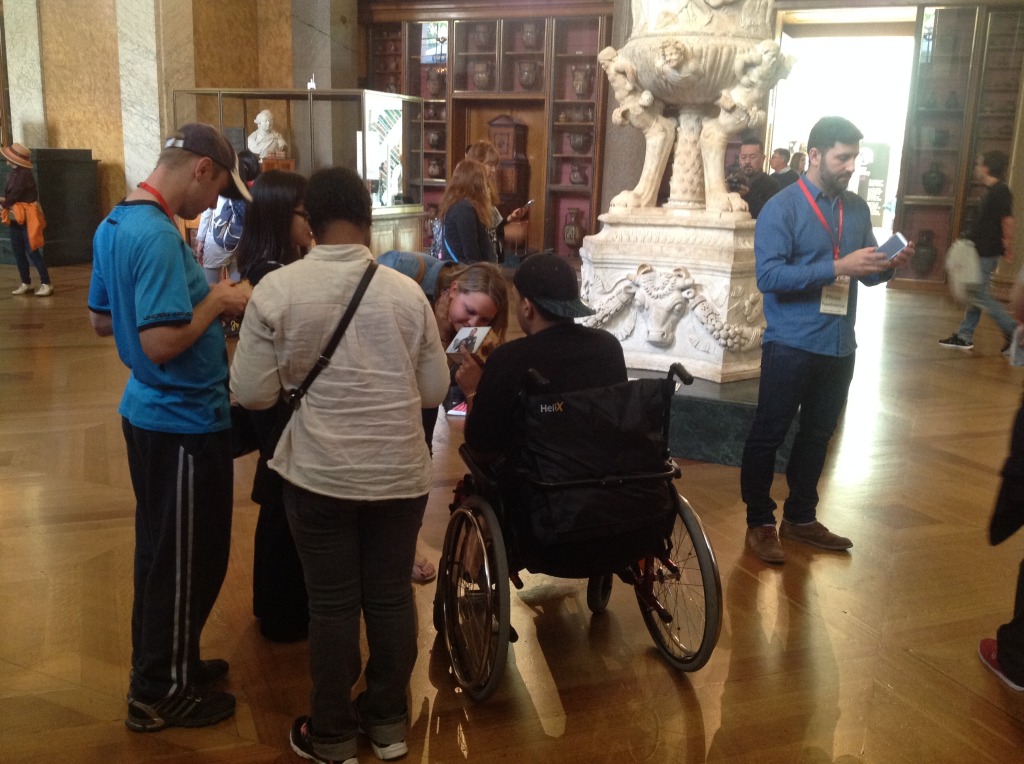
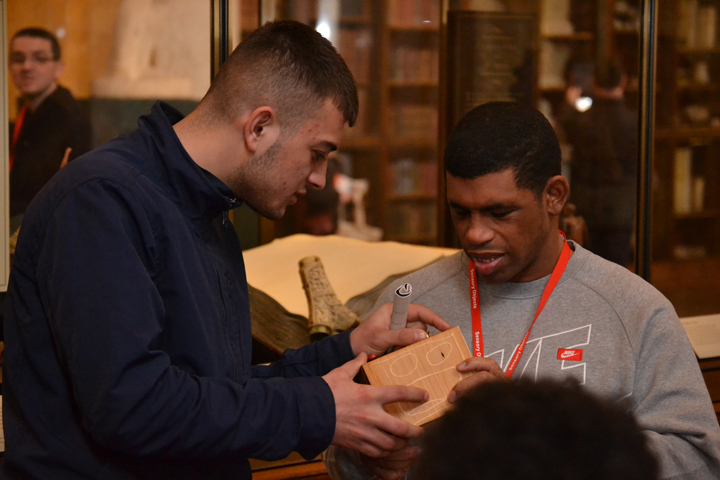
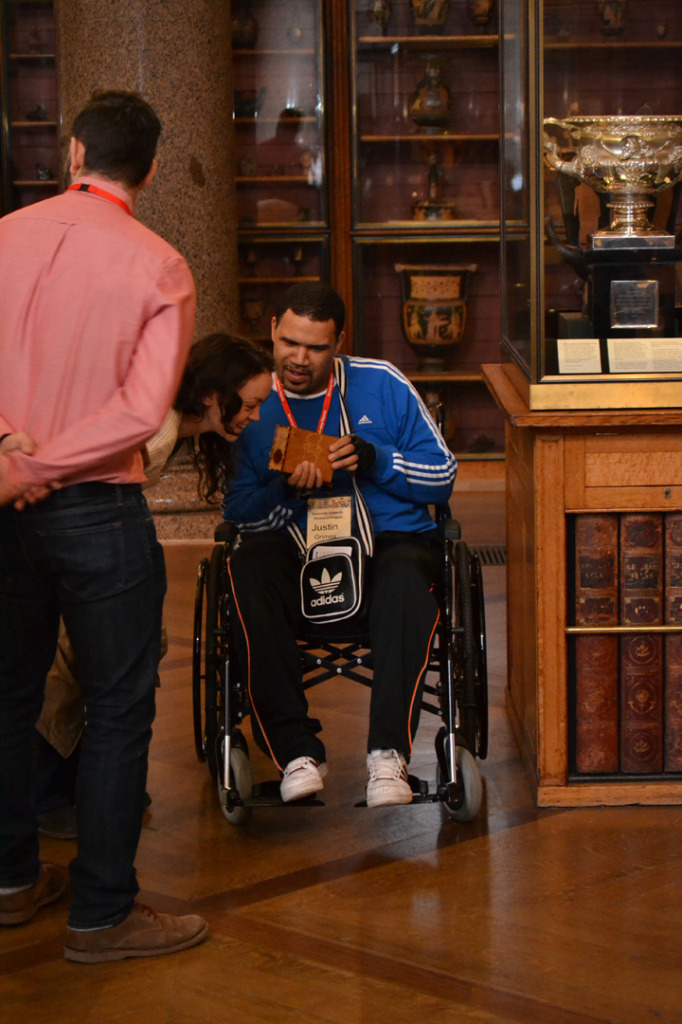
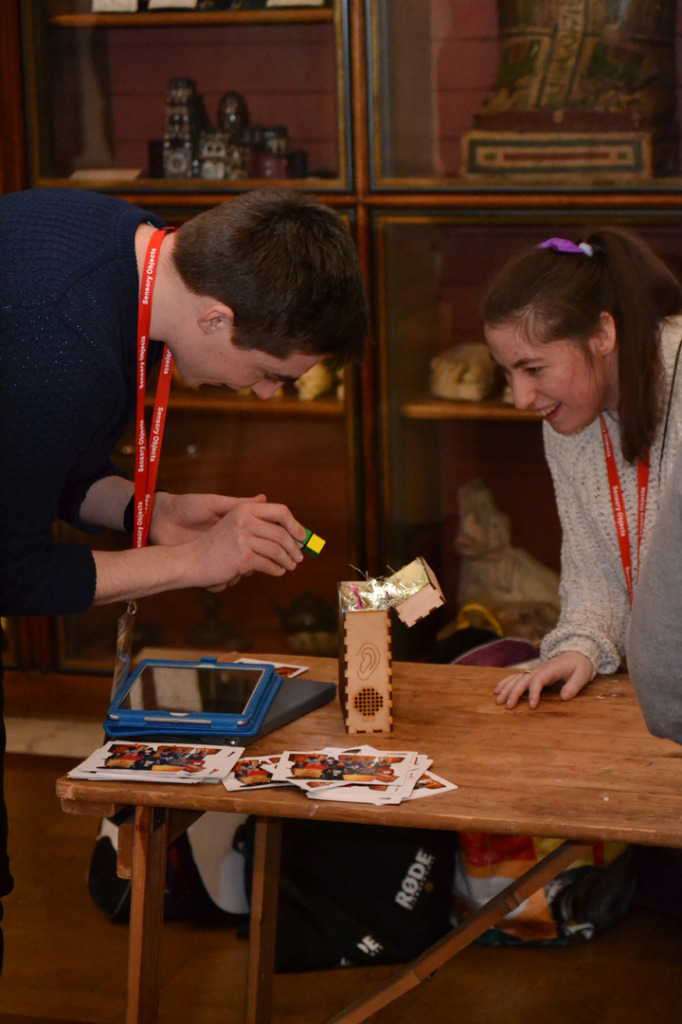
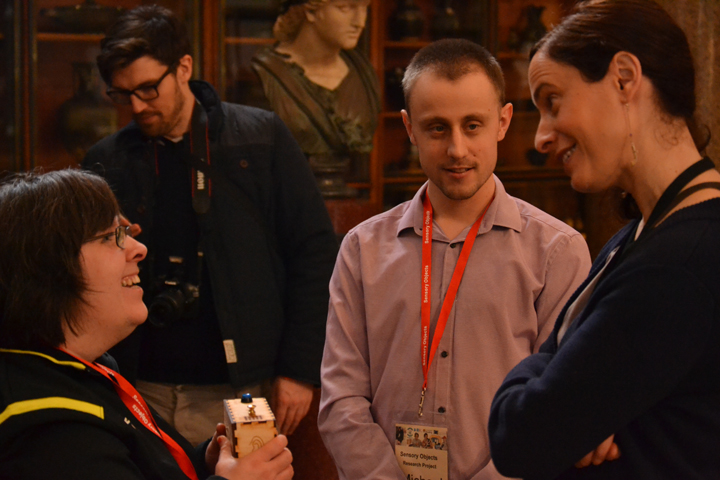
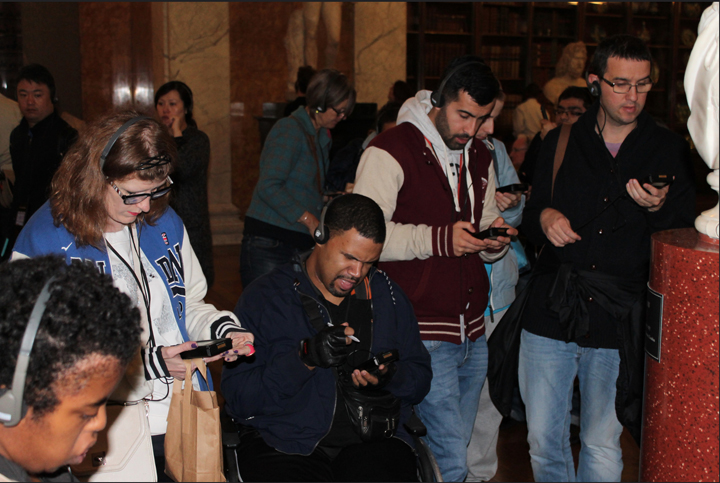
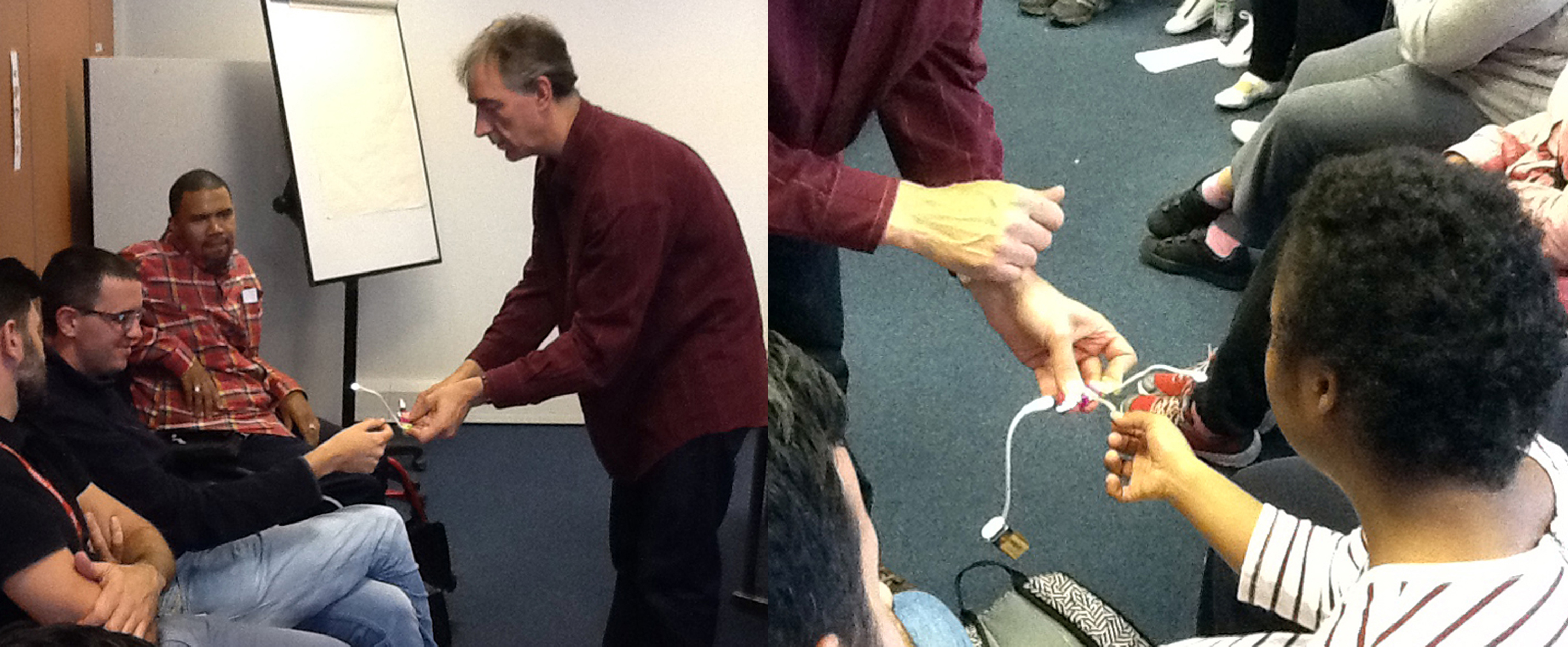
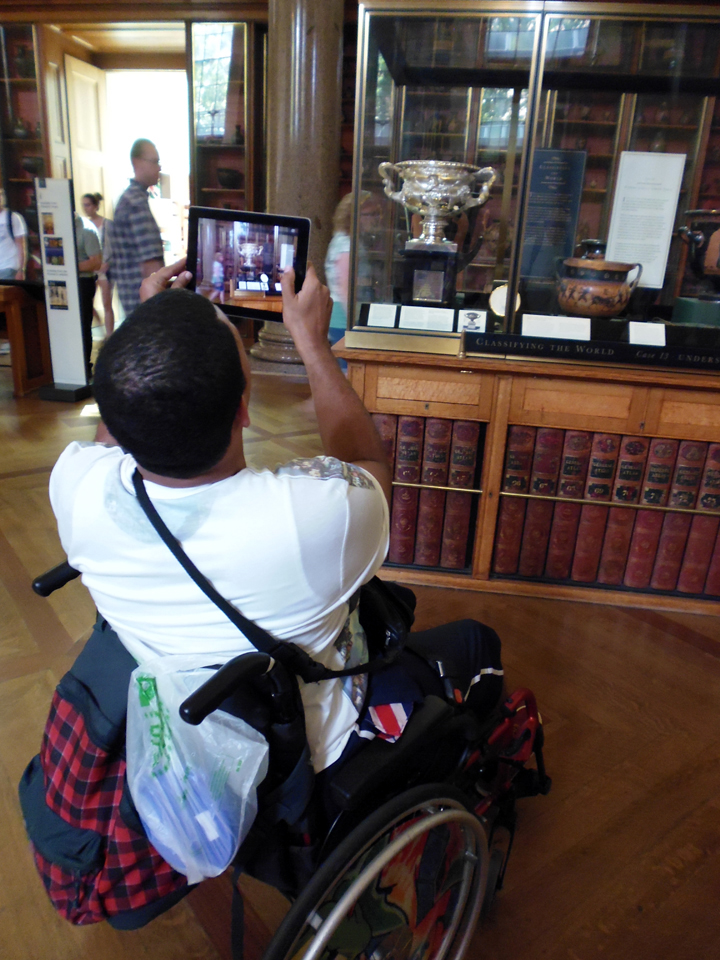
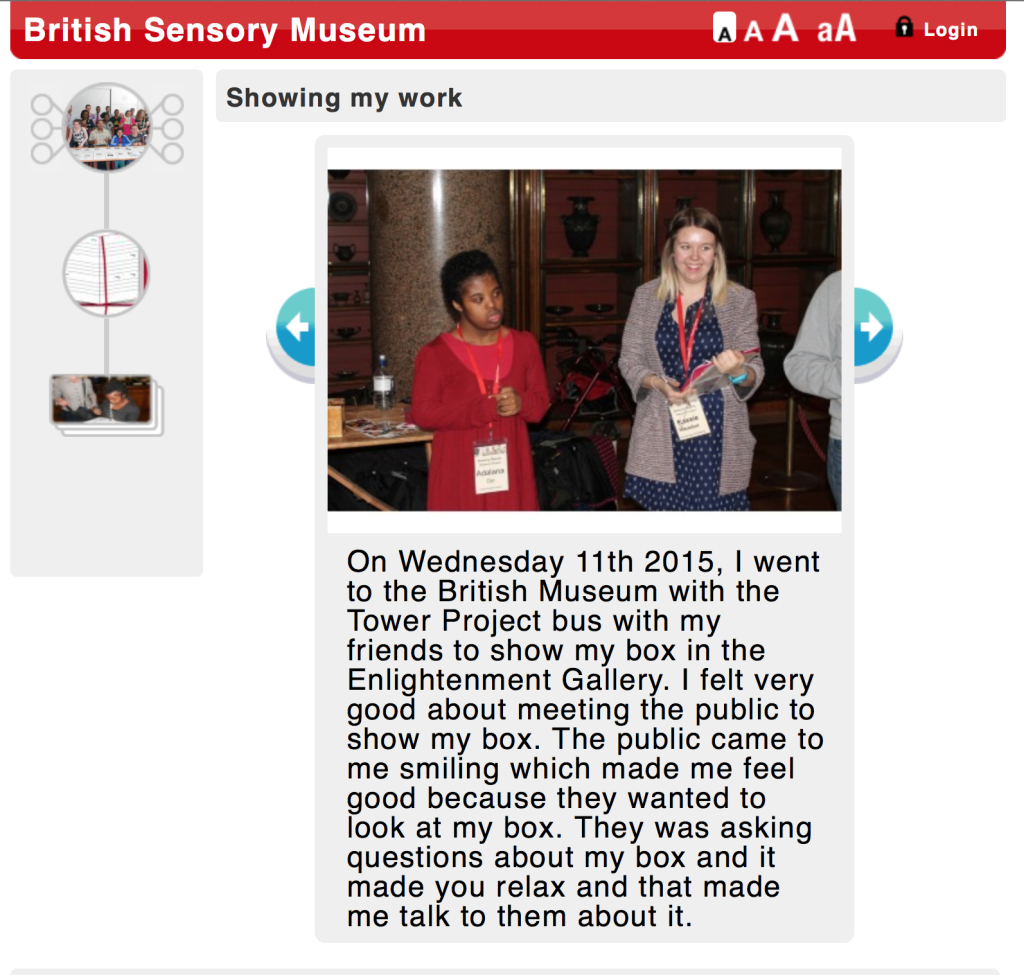
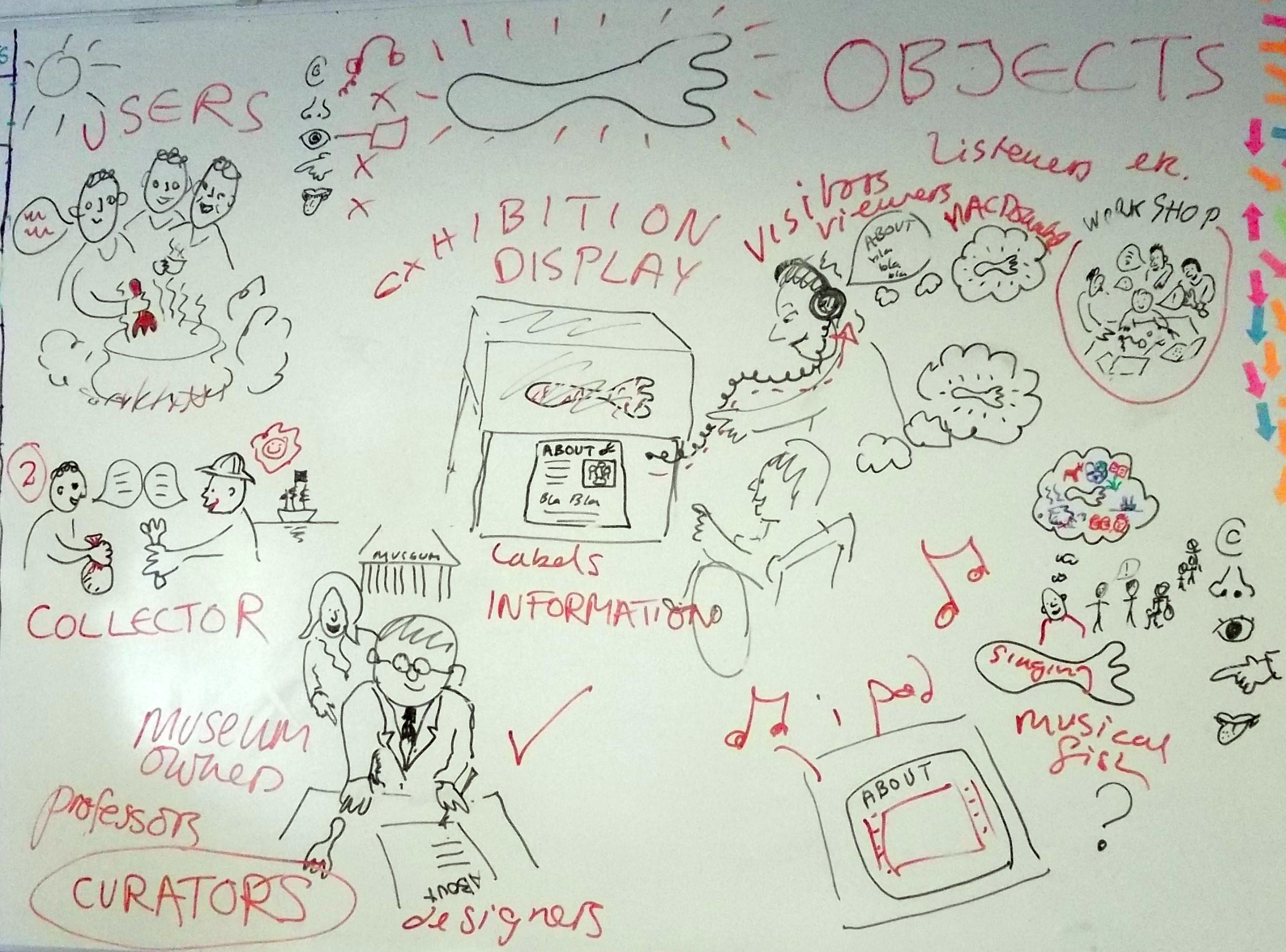
Afterwards Kate and I meet with George Oates from Museum in a Box. I had noticed the similarities between the projects and was intrigued to discuss this further. Both use box formats and readily available low-tech electronics systems. These are easy to use and focus on the non-visual senses (e.g. touch and sound). They encourage people to interact or do something with the objects to make something else happen. Might these devices offer an alternative way of interpreting photographs? Far from being just pictures, we interact with photographs using our emotions and senses. Just think about the photographs in your own house, particularly those of your loved ones. What do they mean to you, and how you display and interact with them? They might make us laugh and cry, and beyond just looking, we touch and respond to photographs in a variety of ways. However this is not how photographs are usually interpreted and displayed in museums. Instead photographs are simply used as images to illustrate historical events and show what people looked like (a form of visual evidence).
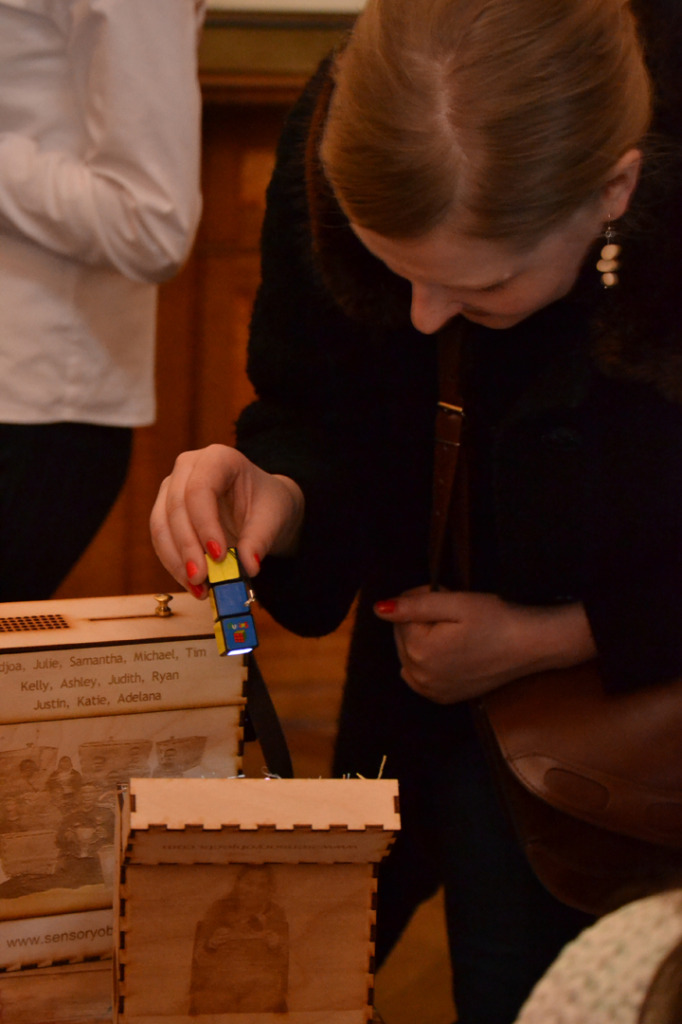
Although Sensory Labels and Museum in a Box are not currently being used to interpret photographs, I can see great potential for this. For example, the laser cut photographs of the creators on the Sensory Labels suggests the way we tend to touch photographs. Touch is important in Māori culture and this technology creates a way of experiencing photographs through the fingertips. Sound is also significant for Māori and with both systems photographs could be used to activate the sound of Māori elders talking. This would give them the opportunity to talk about their ancestors, cultural treasures (known as taonga) and the places shown in the photographs. Themed packs of photographs could also be put together and used as George noted, as a way of ‘returning’ photographs (and the knowledge they hold) of people, places and cultural objects to their communities.
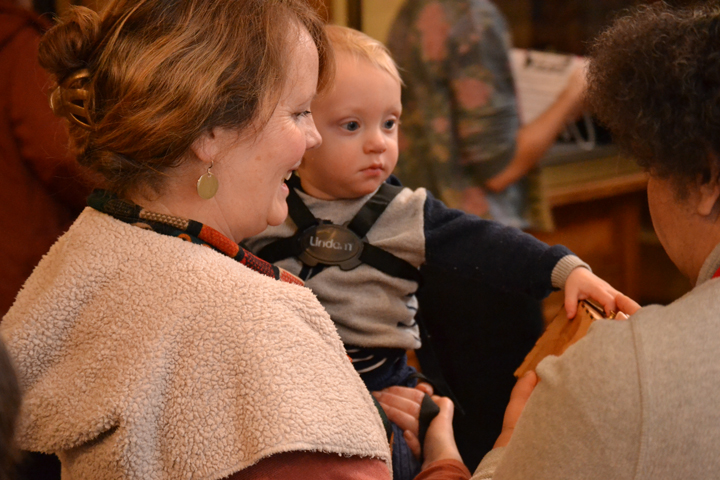
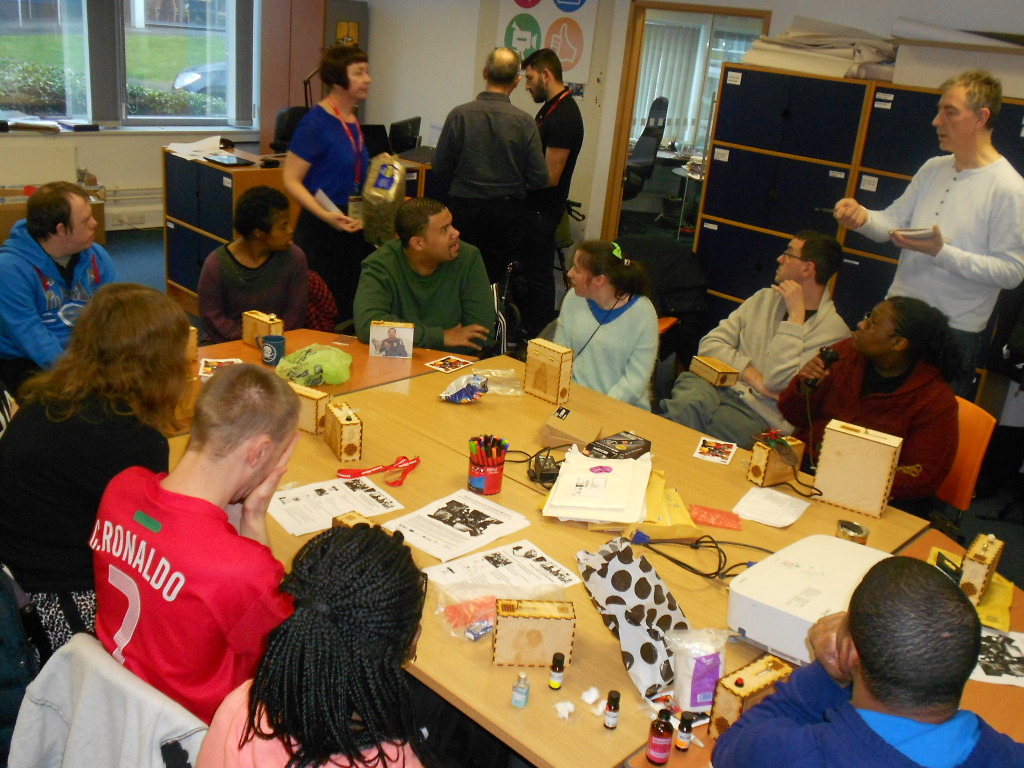
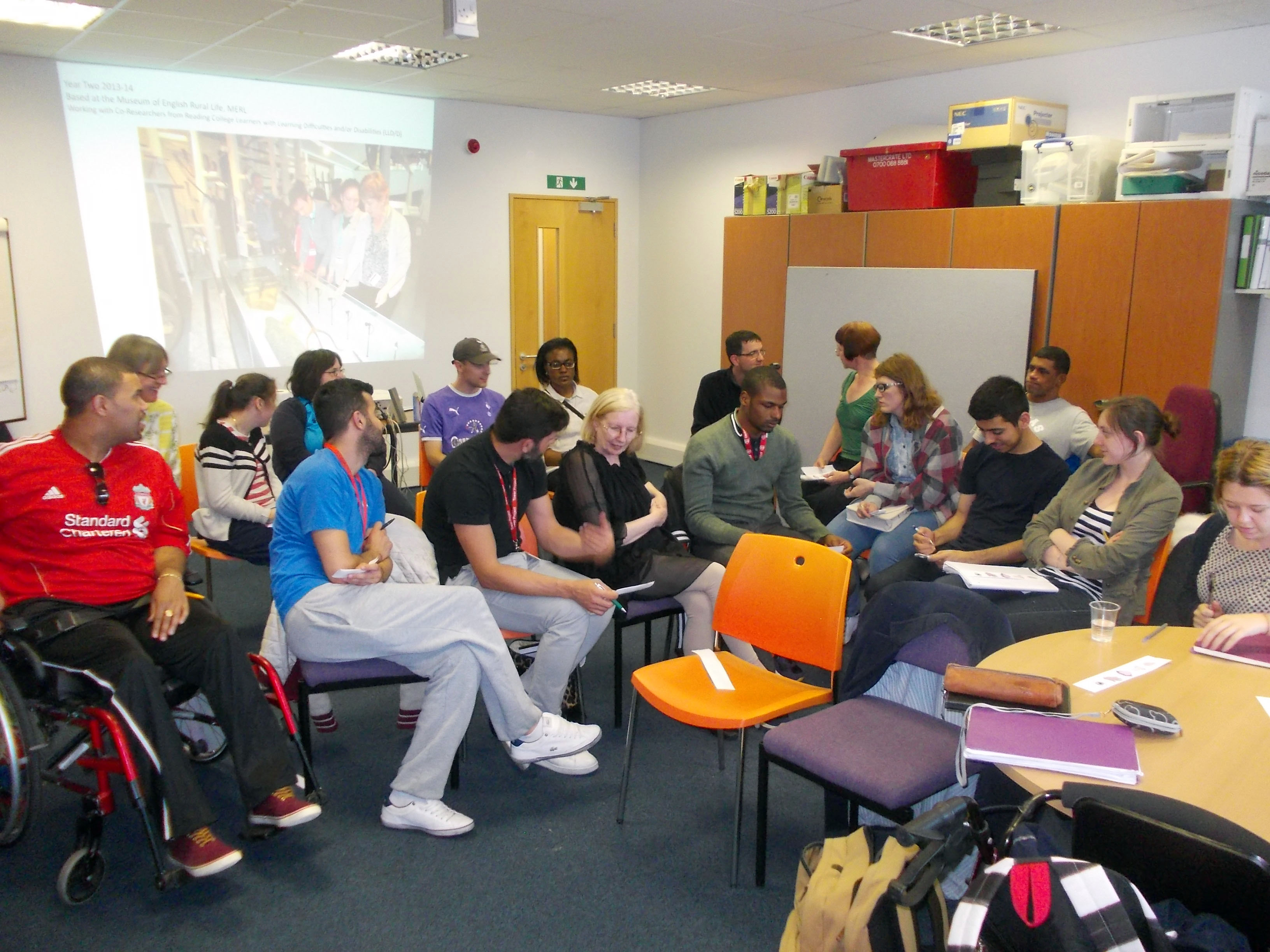
Museum in a Box (foreground) and Sensory Labels (background), 2016. Photograph by Natasha Barrett.
Experiences in museum still tend to rely on looking at and seeing objects. Opportunities for using our other senses, especially with photographs, are still not common. Also, whilst the voices of ordinary people are now heard in museums, these are still often shaped by institutions. Both Sensory Labels and Museum in a Box give people the freedom to express things in their own way. Using low cost systems, they place the power of object interpretation outside of the museum. However, these systems are flexible and can also used within museums. I look forward to seeing how these projects develop in the future!